[ad_1]
New analysis has revealed that the secrets and techniques of the solar’s magnetic discipline, which has remained shrouded in thriller for 4 centuries, might lie near its floor.
The solar’s magnetic discipline is liable for producing darkish patches known as sunspots, erupting photo voltaic flares, and even explosive ejections of matter known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs). But, ever since astronomers started investigating the solar’s magnetic fields, the purpose from which they originate has remained undetermined. Now, a global group of researchers could also be nearer to fixing this 400-year-old thriller that rejected even Galileo Galilei.
The invention implies that sunspots and flares are prone to be the product of a shallow magnetic discipline somewhat than a discipline that originates deeper throughout the solar, one thing that had beforehand been theorized. The group’s findings might assist photo voltaic scientists higher predict photo voltaic flares and geomagnetic storms that pose a danger to Earth’s satellites, communications techniques, and energy infrastructure whereas additionally offering a wierd hyperlink between the outer layers of the solar and feeding black holes.
Associated: The stormy solar erupts with its largest photo voltaic flare but from an enormous sunspot — and it is nonetheless crackling (video)
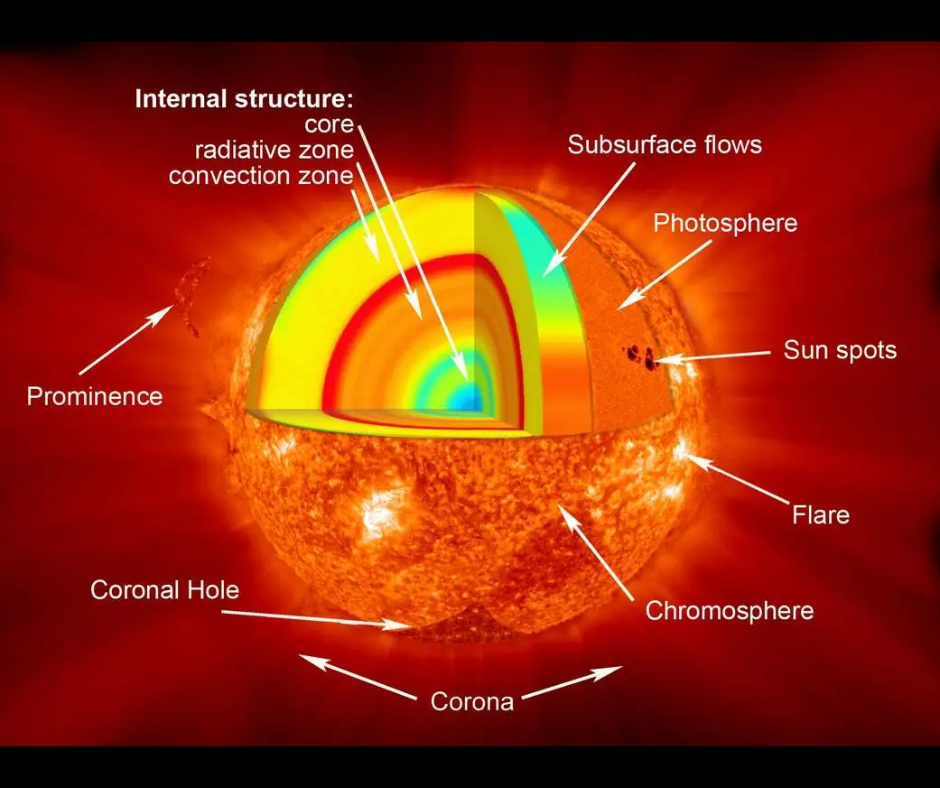
Utilizing a NASA supercomputer, the group behind this analysis carried out a sequence of complicated calculations that confirmed the solar’s magnetic discipline is generated round 40,000 miles (64,000 kilometers) under its floor, the photosphere. This will likely appear extremely deep, however the solar has a radius of round 433,000 miles (697,000 km), that means the magnetic fields are generated within the outer 10% of the solar’s superheated plasma.
“The options we see when trying on the solar, just like the corona that many individuals noticed in the course of the current photo voltaic eclipse, sunspots, and photo voltaic flares, are all related to the solar’s magnetic discipline,” group member Keaton Burns, a analysis scientist on the Massachusetts Institute of Know-how (MIT), mentioned in an announcement. “We present that remoted perturbations close to the solar’s floor, removed from the deeper layers, can develop over time to doubtlessly produce the magnetic buildings we see.”
Sunspots are cool and darkish patches on the floor of the solar that scientists assume are created when magnetic discipline traces tangle. Photo voltaic scientists have discovered sunspots improve in quantity in the course of the photo voltaic most interval of the solar’s 11-year photo voltaic cycle. Observations have proven that sunspots are typically discovered nearer to the equator of the solar somewhat than on the poles of our star.
The photo voltaic dynamo is not that deep
The solar generates its magnetic discipline through a bodily course of that scientists name the photo voltaic dynamo. Earlier fashions of this dynamo have prompt it’s kick-started in a roiling and turbulent area of the solar known as the convection zone. Right here, sizzling plasma rises away from the core of the solar, the place the vast majority of its power is generated, carrying warmth and power to the floor of the solar, the photosphere.
After the power is deposited, the plasma cools and falls again by way of the convection zone, which has a depth of round 124,000 miles (200,000 km) and accounts for round 30% of the solar’s quantity, previous the subsequent “batch” of rising heated plasma.
“One of many primary concepts for learn how to begin a dynamo is that you just want a area the place there’s quite a lot of plasma transferring previous different plasma and that shearing movement converts kinetic power into magnetic power,” Burns defined. “Individuals had thought that the solar’s magnetic discipline is created by the motions on the very backside of the convection zone.”
Different groups of researchers have beforehand created three-dimensional simulations of the solar to mannequin the stream of plasma all through its varied layers and to thus decide the place its magnetic discipline originates. The group argues that these simulations did not pinpoint the true start line of the photo voltaic dynamo as a result of they did not seize the true image of simply how chaotic and turbulent the solar truly is.
Burns and his group took a distinct method. As an alternative of modeling the stream of plasma all through all of the layers within the inside of the solar, they targeted on the steadiness of plasma on the photo voltaic floor. They needed to find out if modifications on this floor area could be sufficient to start out the photo voltaic dynamo.
How the solar’s magnetic fields waft
To start, Burns and colleagues used a course of known as “helioseismology” that measures trapped soundwaves as they ripple by way of the solar and trigger oscillations known as “starquakes” on the photo voltaic floor to find out the inside of the solar. This allowed them to find out the construction and stream of plasma simply beneath the photo voltaic floor.
“Should you take a video of a drum and watch the way it vibrates in gradual movement, you possibly can work out the drumhead’s form and stiffness from the vibrational modes,” Burns mentioned. “Equally, we will use vibrations that we see on the photo voltaic floor to deduce the common construction on the within. These common flows look type like an onion, with completely different layers of plasma rotating previous one another.”
The group turned to the Dedalus Challenge, a framework developed by Burns that may simulate fluid flows with excessive precision, to have a look at this stream of photo voltaic plasma after which see if any tiny modifications or “perturbations” could possibly be launched to the common construction that would develop and trigger the photo voltaic dynamo.
Their algorithm found new patterns within the stream of plasma that may develop and create an image of actual photo voltaic exercise. These patterns matched the areas of sunspots that astronomers have been seeing since 1612 and the observations of Galileo.
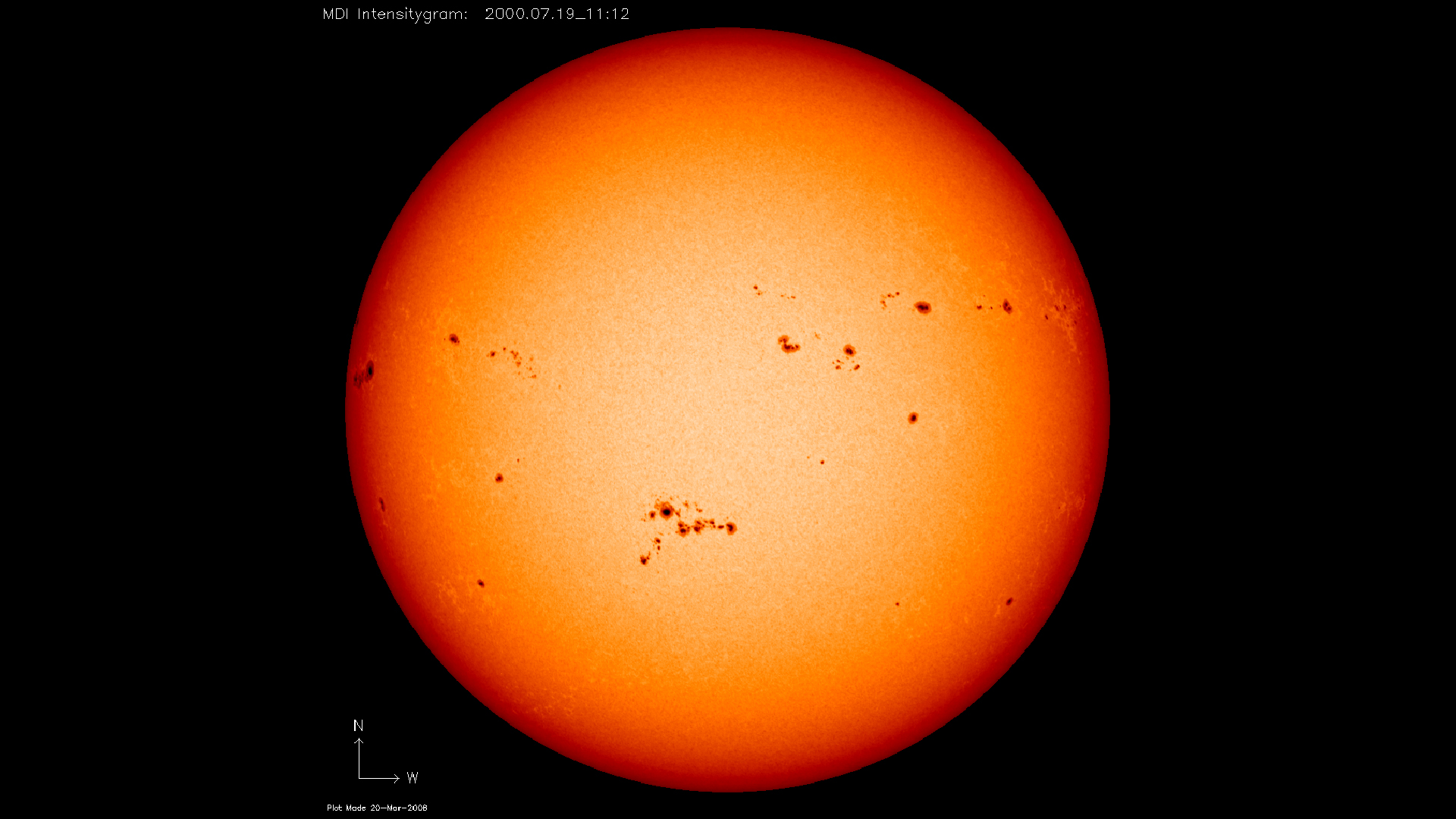
Sunspots are cool and darkish patches on the floor of the solar that scientists assume are created when magnetic discipline traces tangle. Photo voltaic scientists have discovered sunspots improve in quantity in the course of the photo voltaic most interval of the solar’s 11-year photo voltaic cycle. Observations have proven that sunspots are typically discovered nearer to the equator of the solar somewhat than on the poles of our star.
The Dedalus Challenge simulations revealed that modifications in plasma flows within the prime 5% to 10% of the solar have been enough sufficient to generate magnetic buildings that may account for noticed sunspot exercise. After they modeled deeper areas of our star because the supply of magnetic fields, this led to sunspots congregating on the poles of the solar somewhat than its equator, which is the alternative of what’s truly seen by astronomers.
Taking a more in-depth have a look at how plasma flowed on the floor of the solar, Burns and colleagues additionally discovered a stunning similarity to the quick environments of black holes.
A wierd connection between the solar and feeding black holes
When stars enterprise too near black holes, they are often destroyed by large gravitational forces that squash them horizontally and squeeze them vertically, “spaghettifying” them in an prevalence known as a tidal disruption occasion (TDE).
Moreover, in conditions when a star orbits a black gap in a binary system and is both too shut, or its outer layers have “puffed out,” the gravitational affect of the black gap can strip away stellar materials.

In each the circumstances of stellar cannibalism and in much less excessive conditions when black holes are in areas of fuel and mud, this superheated plasma has angular momentum (or spin), and meaning it will possibly’t simply fall into the black gap.
As an alternative, this plasma types a flattened cloud across the black gap that steadily feeds it and is topic to immense frictional forces as a result of gravity of the black gap that heats it, inflicting it to glow. This ‘platter’ of plasma is named an accretion disk. Accretion disks are turbulent and feed black holes due to co-called “magnetorotational instability” of their stream of plasma. This turbulence is created when magnetized materials nearer to the sting of an accretion disk strikes extra slowly than materials nearer to its heart.
Burns and group assume {that a} related phenomenon is occurring within the solar’s magnetic discipline, and it’s this magnetorotational instability within the solar’s outermost layers that is step one in producing the solar’s magnetic discipline.
“I believe this consequence could also be controversial,” Burns added. “A lot of the neighborhood has been targeted on discovering dynamo motion deep within the solar. Now we’re displaying there is a completely different mechanism that appears to be a greater match to observations.”
The group will now proceed their investigation by learning floor magnetic discipline patterns and making an attempt to find out if they’ll create particular person sunspots of their simulations and to find out how they hyperlink to the general 11-year cycle of the solar.
“We all know the dynamo acts like a large clock with many complicated interacting elements,” Geoffrey Vasil, group member and researcher on the College of Edinburgh, mentioned. “However we do not know most of the items or how they match collectively. This new concept of how the photo voltaic dynamo begins is important to understanding and predicting it.”
The group’s analysis was printed on Wednesday (Could 22) within the journal Nature.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

