[ad_1]
Mexico’s Taam Ja’ Blue Gap is the deepest recognized underwater sinkhole on the earth, researchers have found — they usually have not even reached the underside but.
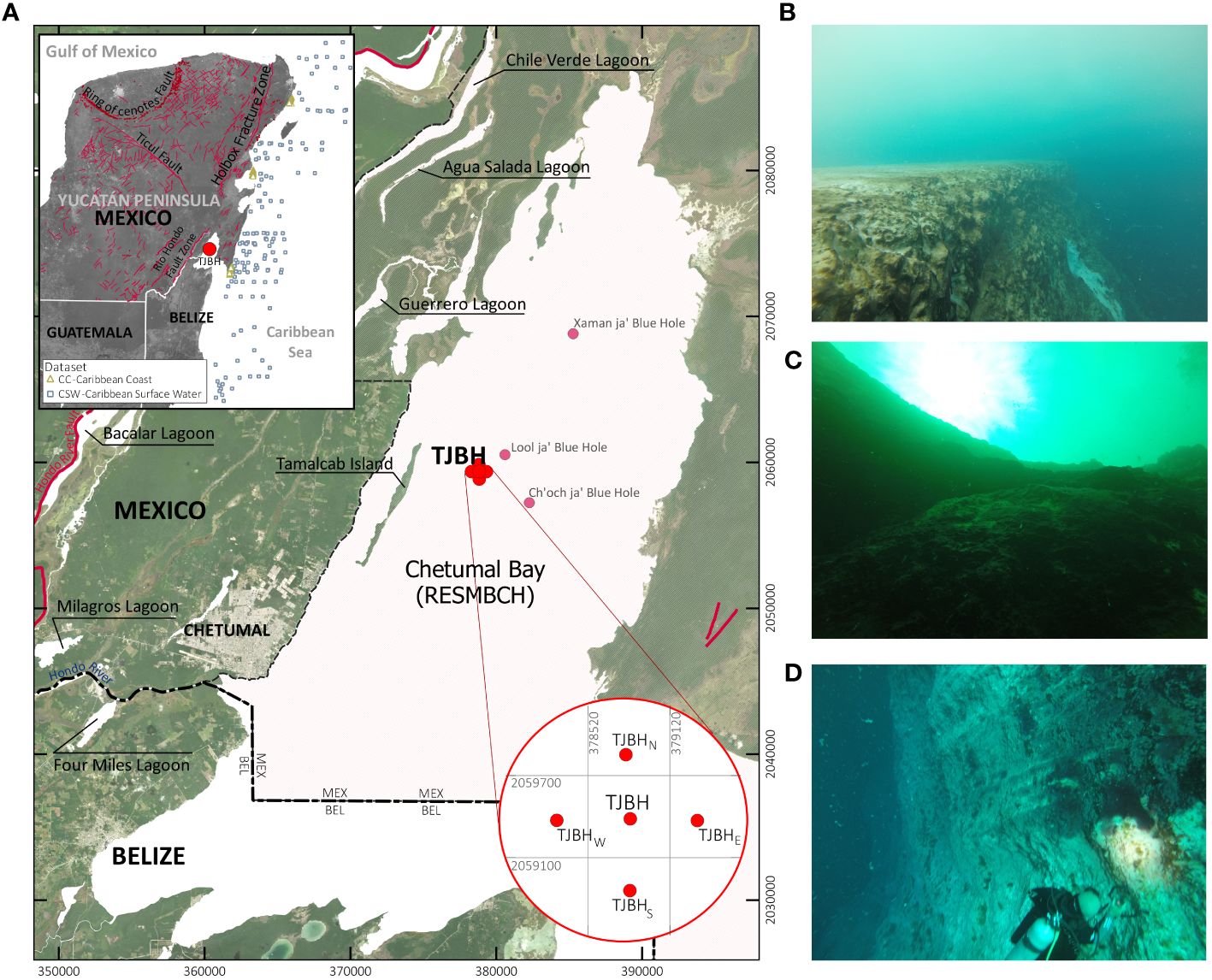
New measurements point out the Taam Ja’ Blue Gap (TJBH), which sits in Chetumal Bay off the southeast coast of the Yucatan Peninsula, extends no less than 1,380 ft (420 meters) beneath sea stage.
That is 480 ft (146 m) deeper than scientists initially documented after they first found the blue gap in 2021, and 390 ft (119 m) deeper than the earlier document holder — the 990-foot-deep (301 m) Sansha Yongle Blue Gap, often known as the Dragon Gap, within the South China Sea.
“On December 6, 2023, a scuba diving expedition was carried out to establish the environmental circumstances prevailing on the TJBH,” researchers wrote in a research printed Monday (April 29) within the journal Frontiers in Marine Science. Through the expedition, the researchers took measurements with a conductivity, temperature and depth (CTD) profiler — a tool with a set of probes that learn and transmit water properties to the floor in actual time through a cable. The information revealed that the Taam Ja’ blue gap is “the world’s deepest recognized blue gap, with its backside nonetheless not reached,” the researchers wrote within the research.
Associated: Colossal collapse Mexico that shaped 15 million years in the past is much more monumental than we thought
The profiler additionally highlighted totally different layers of water inside the blue gap, together with a layer beneath 1,312 ft (400 m) the place the temperature and salinity circumstances resembled these of the Caribbean Sea and close by coastal reef lagoons. This means the TJBH could also be related to the ocean through a hidden community of tunnels and caves, in line with the research.
Blue holes are water-filled vertical caverns, or sinkholes, present in coastal areas the place the bedrock is made from soluble materials, equivalent to limestone, marble or gypsum. They type when water on the floor percolates via the rock, dissolving minerals and widening cracks, which ultimately causes the rock to break down. Well-known examples embrace Dean’s Blue Gap within the Bahamas, the Dahab Blue Gap in Egypt and the Nice Blue Gap in Belize.
Preliminary measurements of the TJBH had been taken utilizing an echo sounder — an instrument that sends sound waves all the way down to the underside of the water and measures the pace they arrive again to calculate distance. Nonetheless, there are limitations to echo sounding methods in blue holes as a consequence of fluctuations in water density and the unpredictable form of every gap, which is probably not completely vertical.
“Affirmation of the utmost depth was not doable as a consequence of instrument limitations through the scientific expeditions in 2021,” the researchers wrote within the research.
The CTD instrument used for the current work didn’t discover the underside of the blue gap both, because it might solely function all the way down to depths of 1,640 ft (500 m). Scientists lowered the profiler all the way down to that depth, however the cable it was hooked up to could have drifted on underwater currents or bumped right into a ledge that stopped the gadget in its tracks 1,380 ft down, in line with the research.
Subsequent, the scientists plan to”decipher TJBH’s “most depth and the probabilities of forming a part of an underwater intricate and probably interconnected system of caves and tunnels,” the researchers wrote.
“Inside the depths of TJBH might additionally lie a biodiversity to be explored,” they added.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

