[ad_1]
UC San Diego researchers have linked lipid metabolism modifications to Alzheimer’s illness development, figuring out potential new remedies by focusing on the AMPK enzyme to disrupt a cycle of mind irritation.
Researchers at UC San Diego have utilized superior imaging methods to discover the metabolic processes behind Alzheimer’s illness, resulting in potential new methods for therapy.
Alzheimer’s illness, the commonest kind of dementia, considerably impairs reminiscence, considering, and habits, affecting over 50 million folks globally every year. Projections counsel that this quantity will triple by 2050.
Utilizing their very own state-of-the-art imaging applied sciences, scientists on the College of California San Diego have now revealed how the metabolism of lipids, a category of molecule that features fat, oils, and plenty of hormones, is modified in Alzheimer’s illness. Additionally they revealed a brand new technique to focus on this metabolic system with new and present medication. The findings are revealed in Cell Metabolism.
“Lipids have been related to Alzheimer’s for so long as we’ve recognized concerning the illness,” stated senior and co-corresponding creator Xu Chen, Ph.D., an assistant professor within the Division of Neurosciences at UC San Diego Faculty of Medication, referring to the unique 1907 report by Alois Alzheimer that described the weird presence of fats deposits within the mind of the primary particular person to be recognized with the illness. “A lot of the emphasis since then has been positioned on tau and different proteins that the analysis group has, till the final decade or so, largely neglected this necessary facet of the illness.”
Modern Imaging Methods
“Pushed by a eager curiosity in lipid droplet capabilities in growing old and illness, we initiated this fruitful collaboration to harness cutting-edge SRS know-how for learning lipid metabolism in tauopathy mouse brains.” Mentioned Yajuan Li, M.D., Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher within the Shu Chien-Gene Lay Division of Bioengineering at UC San Diego Jacobs Faculty of Engineering. SRS imaging is an method that analyzes the best way molecules in a pattern work together with laser mild.
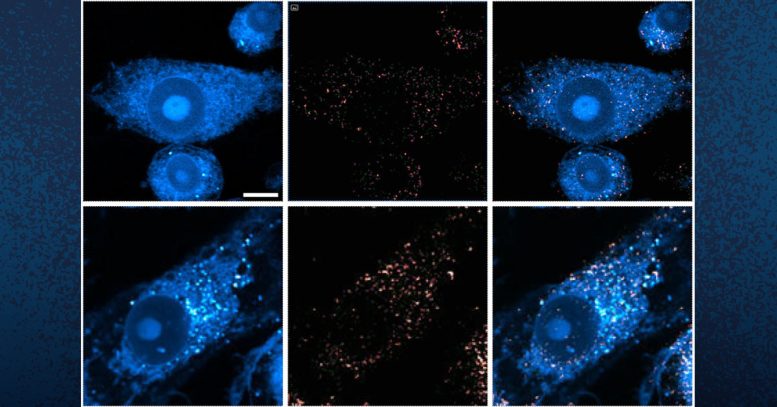
These photographs present microglia containing lipid droplets (white spots). Researchers at UC San Diego have revealed that in brains with Alzheimer’s and associated illnesses, neurons offload extra lipid droplets to microglia, which triggers additional irritation. Credit score: UC San Diego Well being Sciences
Within the mind, lipids come within the type of tiny droplets that management quite a lot of processes, reminiscent of vitality storage and mobile responses to emphasize. These processes are tightly regulated in typical brains, however in Alzheimer’s or related illnesses, lipid droplet metabolism can malfunction. Whereas scientists perceive that there’s a relationship between Alzheimer’s and lipid metabolism, precisely how they affect each other has remained a thriller.
To reply this query, the group appeared instantly at lipid droplets within the brains of mice with extra tau protein. They used a state-of-the-art SRS imaging platform developed in Lingyan Shi’s lab on the Jacobs Faculty of Engineering. The platform makes it doable to take microscopic photographs of lipid droplets inside cells with out the usage of chemical dyes, which may alter the fragile molecules and compromise the outcomes.
Mechanisms and Implications
“Intriguingly, the inert lipid droplets noticed in tauopathy brains exhibit related habits to these present in growing old brains”, stated co-corresponding creator Lingyan Shi, Ph.D., assistant professor of bioengineering on the Jacobs Faculty. “We are actually specializing in understanding the underlying mechanisms by combining SRS imaging with different using multidisciplinary methods. Our method is biologically impartial, so we’re in a position to observe what’s occurring within the mind on the molecular stage with as little interference as doable.”
Shi and her group, together with Li, pioneered the brand new method, which makes use of a specifically modified model of water, known as heavy water, as a metabolic probe.
“As an alternative of utilizing a typical chemical dye to stain lipids, we use heavy water that’s naturally taking part within the metabolic actions we’re keen on,” added Shi. “This provides us a a lot clearer image of how lipids are shaped spatiotemporally, which might not be doable with different approaches. Our present focus is on comprehending the underlying mechanisms of those dynamic modifications of lipid metabolism within the context of growing old and illnesses.”
The researchers found that in brains with tauopathy, neurons accumulate extra lipids on account of stress or harm. This inflow forces neurons to dump the surplus to immune cells within the mind, known as microglia. These microglia then mount an inflammatory response that causes additional stress to neurons, triggering a repeating and worsening cycle.
Along with characterizing this course of, they had been additionally in a position to establish a essential enzyme, known as adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) that orchestrates the cycle. In line with the researchers, breaking this cycle may unlock new therapy choices for Alzheimer’s illness. Chen is especially optimistic about the potential of repurposing present medication that modify lipid metabolism.
“We don’t suppose that is an incidental phenomenon,” stated Chen. “The proof means that lipid metabolism is a driving mechanism for Alzheimer’s illness. There are numerous medication that concentrate on lipid metabolism in different physique techniques, reminiscent of within the liver, so we would have the ability to change this technique fairly dramatically utilizing instruments we have already got.”
Reference: “Microglial lipid droplet accumulation in tauopathy mind is regulated by neuronal AMPK” by Yajuan Li, Daniel Munoz-Mayorga, Yuhang Nie, Ningxin Kang, Yuren Tao, Jessica Lagerwall, Carla Pernaci, Genevieve Curtin, Nicole G. Coufal, Jerome Mertens, Lingyan Shi and Xu Chen, 23 April 2024, Cell Metabolism.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.03.014
This work was funded, partially, by the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (grants R01AG074273, R01AG078185, 1R01GM149976-01, R01NS111039 R21NS125395) and by the startup fund from UC San Diego Division of Neurosciences and Jacob Faculty of Engineering.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

