[ad_1]
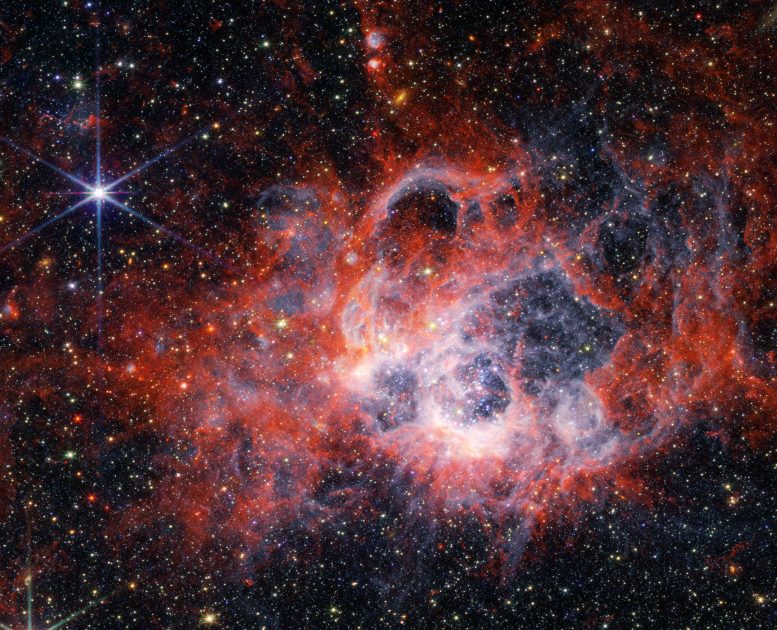

This picture from NASA’s James Webb House Telescope’s NIRCam (Close to-Infrared Digital camera) of the star-forming area NGC 604 reveals how stellar winds from vivid, scorching younger stars carve out cavities in surrounding gasoline and mud. Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
Distinctive Alternative To Research Excessive Focus of Large, Younger Stars Close by
Within the astronomy area, the time period “close by” is sort of relative. Neighboring galaxies to our house galaxy, the Milky Approach, are just a few million light-years away. In distinction, a few of the most distant galaxies ever detected, nearer to the Large Bang, are billions of light-years away. In some instances, the power to review close by objects at a particularly excessive decision might help astronomers higher perceive extra distant objects.
Take the star-forming area NGC 604 as one instance. Positioned 2.73 million light-years away within the close by Triangulum galaxy, this area is much like acquainted starbirth areas in our Milky Approach galaxy, such because the Orion Nebula, however it’s a lot bigger in extent and incorporates many extra just lately shaped stars. Such areas are small-scale variations of extra distant “starburst” galaxies, which underwent a particularly excessive price of star formation.
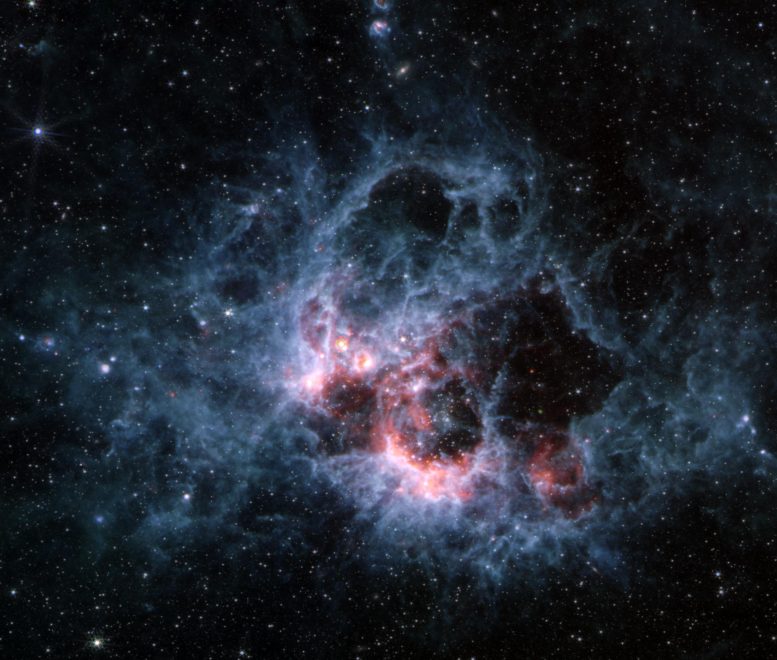

This picture from NASA’s James Webb House Telescope’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) of star-forming area NGC 604 reveals how massive clouds of cooler gasoline and mud glow in mid-infrared wavelengths. This area is a hotbed of star formation and residential to greater than 200 of the most popular, most large sorts of stars, all within the early levels of their lives. Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
Peering Into the Tendrils of NGC 604 With NASA’s Webb House Telescope
The formation of stars and the chaotic environments they inhabit is without doubt one of the most well-studied, but additionally mystery-shrouded, areas of cosmic investigation. The intricacies of those processes are actually being unveiled like by no means earlier than by NASA’s James Webb House Telescope.
Two new photos from Webb’s NIRCam (Close to-Infrared Digital camera) and MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) showcase star-forming area NGC 604, positioned within the Triangulum galaxy (M33), 2.73 million light-years away from Earth. In these photos, cavernous bubbles and stretched-out filaments of gasoline etch a extra detailed and full tapestry of star start than seen previously.
Insights Into NGC 604
Sheltered amongst NGC 604’s dusty envelopes of gasoline are greater than 200 of the most popular, most large sorts of stars, all within the early levels of their lives. Some of these stars are B-types and O-types, the latter of which might be greater than 100 instances the mass of our personal Solar. It’s fairly uncommon to search out this focus of them within the close by universe. In actual fact, there’s no comparable area inside our personal Milky Approach galaxy.
This focus of large stars, mixed with its comparatively shut distance, means NGC 604 supplies astronomers with a chance to review these objects at an enchanting time early of their life.
This video compares photos of star-forming area NGC 604 taken in seen gentle with the Hubble House Telescope’s WFPC2 (Broad Subject and Planetary Digital camera 2), near-infrared with the James Webb House Telescope’s NIRCam (Close to-Infrared Digital camera), and mid-infrared with Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument). Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, Alyssa Pagan (STScI)
Webb’s Close to-Infrared and Mid-Infrared Observations
In Webb’s near-infrared NIRCam picture (picture at prime of web page), essentially the most noticeable options are tendrils and clumps of emission that seem vivid purple, extending out from areas that appear like clearings, or massive bubbles within the nebula. Stellar winds from the brightest and hottest younger stars have carved out these cavities, whereas ultraviolet radiation ionizes the encircling gasoline. This ionized hydrogen seems as a white and blue ghostly glow.
The brilliant orange-colored streaks within the Webb near-infrared picture signify the presence of carbon-based molecules often called polycyclic fragrant hydrocarbons, or PAHs. This materials performs an necessary position within the interstellar medium and the formation of stars and planets, however its origin is a thriller. As you journey farther from the rapid clearings of mud, the deeper purple signifies molecular hydrogen. This cooler gasoline is a chief setting for star formation.
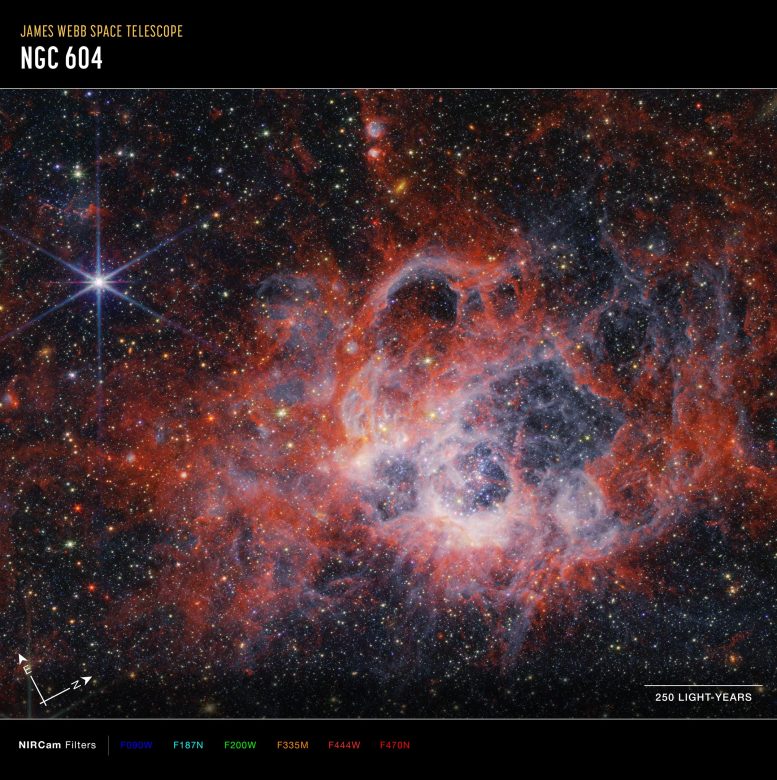
This picture of the NGC 604, captured by Webb’s NIRCam (Close to-Infrared Digital camera) reveals compass arrows, scale bar, and coloration key for reference.
The north and east compass arrows present the orientation of the picture on the sky.
The dimensions bar is labeled in light-years, which is the space that gentle travels in a single Earth-year. (It takes 3 years for gentle to journey a distance equal to the size of the dimensions bar). One light-year is the same as about 5.88 trillion miles or 9.46 trillion kilometers.
This picture reveals invisible near-infrared wavelengths of sunshine which were translated into visible-light colours. The colour key reveals which NIRCam filters had been used when amassing the sunshine. The colour of every filter title is the seen gentle coloration used to symbolize the infrared gentle that passes by way of that filter.
Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
Webb’s beautiful decision additionally supplies insights into options that beforehand appeared unrelated to the primary cloud. For instance, in Webb’s picture, there are two vivid, younger stars carving out holes in mud above the central nebula, related by way of diffuse purple gasoline. In visible-light imaging from NASA’s Hubble House Telescope, these appeared as separate splotches.
Webb’s view in mid-infrared wavelengths additionally illustrates a brand new perspective into the varied and dynamic exercise of this area. Within the MIRI view of NGC 604 (2nd picture from prime of web page), there are noticeably fewer stars. It’s because scorching stars emit a lot much less gentle at these wavelengths, whereas the bigger clouds of cooler gasoline and mud glow. A number of the stars seen on this picture, belonging to the encircling galaxy, are purple supergiants – stars which might be cool however very massive, lots of of instances the diameter of our Solar. Moreover, a few of the background galaxies that appeared within the NIRCam picture additionally fade. Within the MIRI picture, the blue tendrils of fabric signify the presence of PAHs.
NGC 604 is estimated to be round 3.5 million years outdated. The cloud of glowing gases extends to some 1,300 light-years throughout.
The James Webb House Telescope is the world’s premier area science observatory. Webb is fixing mysteries in our photo voltaic system, trying past to distant worlds round different stars, and probing the mysterious buildings and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is a global program led by NASA with its companions, ESA (European House Company) and the Canadian House Company.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

