[ad_1]
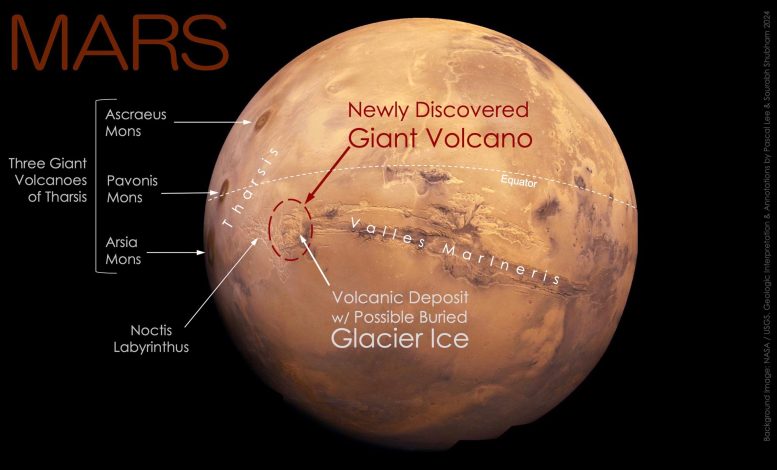
Determine 1: A large volcano hiding in plain sight in considered one of Mars’ most iconic areas.
The newly found big volcano on Mars is situated simply south of the planet’s equator, in Jap Noctis Labyrinthus, west of Valles Marineris, the planet’s huge canyon system. The volcano sits on the jap fringe of a broad regional topographic rise referred to as Tharsis, house to a few different well-known big volcanoes: Ascraeus Mons, Pavonis Mons, and Arsia Mons. Though extra eroded and fewer excessive than these giants, the newly found volcano rivals the others in diameter, which is about 450 km (280 miles) (pink dashed circle on this image). Doable buried glacier ice can be reported beneath a comparatively latest volcanic deposit throughout the perimeter of the eroded volcano, making the world enticing for the seek for life and future robotic and human exploration.
Credit score: Background picture: NASA/USGS Mars globe. Geologic interpretation and annotations by Pascal Lee and Sourabh Shubham 2024.
A deeply eroded big volcano, lively from historic by way of latest occasions and with potential remnants of glacier ice close to its base, had been hiding close to Mars’ equator in plain sight. Its discovery factors to an thrilling new place to seek for life, and a possible vacation spot for future robotic and human exploration.
In a groundbreaking announcement on the fifty fifth Lunar and Planetary Science Convention held in The Woodlands, Texas, scientists revealed the invention of a large volcano and potential sheet of buried glacier ice within the jap a part of Mars’ Tharsis volcanic province, close to the planet’s equator. Imaged repeatedly by orbiting spacecraft round Mars since Mariner 9 in 1971 — however deeply eroded past straightforward recognition, the enormous volcano had been hiding in plain sight for many years in considered one of Mars’ most iconic areas, on the boundary between the closely fractured maze-like Noctis Labyrinthus (Labyrinth of the Evening) and the monumental canyons of Valles Marineris (Valleys of Mariner) (Fig. 1).
Insights Into Noctis Volcano
Provisionally designated “Noctis volcano” pending an official title, the construction is centered at 7° 35′ S, 93° 55′ W. It reaches +9022 meters (29,600 ft) in elevation and spans 450 kilometers (280 miles) in width. The volcano’s gigantic measurement and sophisticated modification historical past point out that it has been lively for a really very long time. In its southeastern half lies a skinny, latest volcanic deposit beneath which glacier ice is probably going nonetheless current. This mixed big volcano and potential glacier ice discovery is critical, because it factors to an thrilling new location to check Mars’ geologic evolution by way of time, seek for life, and discover with robots and people sooner or later (Fig.2).
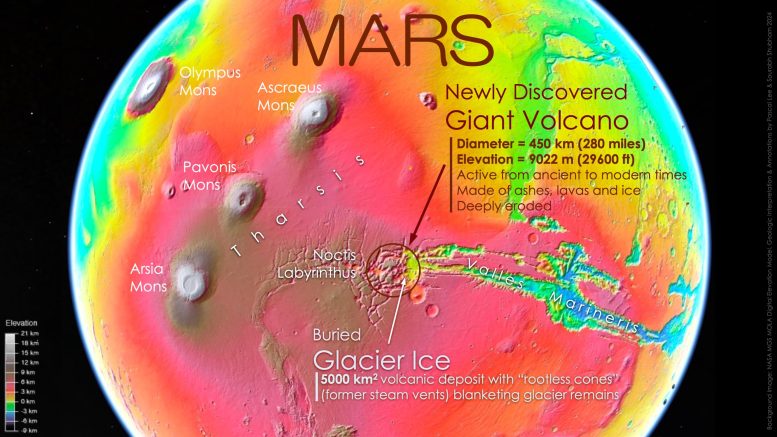
Determine 2. Newly found big volcano is situated within the “center of the motion” on Mars.
Topographic map exhibiting the enduring location of the Noctis volcano between the biggest volcanic and canyon provinces on Mars.
Credit score: Background picture: NASA Mars World Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) digital elevation mannequin. Geologic interpretation & annotations by Pascal Lee and Sourabh Shubham 2024.
“We had been analyzing the geology of an space the place we had discovered the stays of a glacier final yr once we realized we had been inside an enormous and deeply eroded volcano,” mentioned Dr. Pascal Lee, planetary scientist with the SETI Institute and the Mars Institute based mostly at NASA Ames Analysis Middle, and the lead writer of the research.
A number of clues, taken collectively, give away the volcanic nature of the jumble of layered mesas and canyons on this jap a part of Noctis Labyrinthus. The central summit space is marked by a number of elevated mesas forming an arc, reaching a regional excessive and sloping downhill away from the summit space. The light outer slopes lengthen out to 225 kilometers (140 miles) away in numerous instructions. A caldera remnant – the stays of a collapsed volcanic crater as soon as host to a lava lake – might be seen close to the middle of the construction. Lava flows, pyroclastic deposits (made from volcanic particulate supplies resembling ash, cinders, pumice, and tephra), and hydrated mineral deposits happen in a number of areas throughout the construction’s perimeter (Figs. 3, 4, and 5).
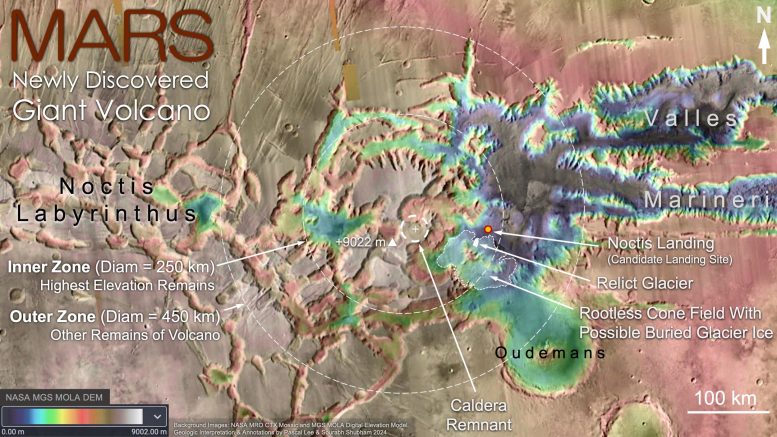
Determine 3: Topographic map of the Noctis volcano.
The Noctis volcano doesn’t current the standard cone form of a typical volcano as a result of an extended historical past of deep fracturing and erosion has modified it. Nonetheless, upon shut inspection, key options indicative of a volcano are recognizable. Inside the “internal zone” delineating the best elevation stays of the volcano, an arc of excessive mesas marks the central summit space, culminating at +9022 m (29,600 ft). Preserved parts of the volcano’s flanks lengthen downhill in numerous instructions to the outer fringe of the “outer zone,” 225 km (140 miles) away from the summit space. A caldera remnant – the stays of a collapsed volcanic crater as soon as host to a lava lake – might be seen close to the middle of the construction. Lava flows, pyroclastic deposits (made from volcanic particulate supplies resembling ash, cinders, pumice and tephra) and hydrothermal mineral deposits happen in a number of areas throughout the perimeter of the volcanic construction. The map additionally reveals the rootless cone subject and potential extent of shallow buried glacier ice reported on this research, in relation to the “relict glacier” found in 2023. Noctis Touchdown, a candidate touchdown website for future robotic and human exploration, can be proven.
Credit score: Background pictures: NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) Context Digital camera (CTX) mosaic and Mars World Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) digital elevation mannequin. Geologic interpretation & annotations by Pascal Lee & Sourabh Shubham 2024.
“This space of Mars is understood to have all kinds of hydrated minerals spanning an extended stretch of Martian historical past. A volcanic setting for these minerals had lengthy been suspected. So, it will not be too stunning to discover a volcano right here,” defined Sourabh Shubham, a graduate scholar on the College of Maryland’s Division of Geology and the research’s co-author. “In some sense, this huge volcano is a long-sought ‘smoking gun’.”
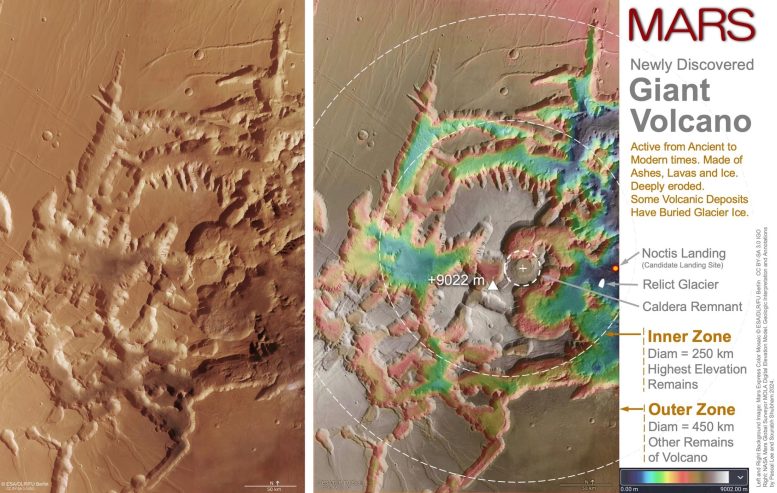
Determine 4: Detailed Mars information evaluation revealed the Noctis volcano.
Detailed evaluation of the altimetry of the area utilizing NASA’s Mars World Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) information, together with excessive decision imaging information from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) Excessive Decision Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) and Context Imager (CTX), and from the European Area Company’s Mars Categorical (MEX) Excessive Decision Stereo Digital camera (HRSC) enabled the invention of the Noctis volcano. Along with the volcano’s summit, caldera remnant, and internal and outer zones, the topographic map on the suitable reveals the “relict glacier” found in 2023 and Noctis Touchdown, a candidate touchdown website for future robotic and human exploration.
Credit score: Left: Mars Categorical HRSC colour mosaic © ESA/DLR/FU Berlin CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO; Proper: Background picture: identical as Left; NASA MGS MOLA digital elevation mannequin. Geologic interpretation and annotations by Pascal Lee and Sourabh Shubham 2024.
Volcanic Terrain and Glacier Remnants
Along with the volcano, the research reviews the invention of a big, 5000 sq. kilometer (1930 sq. mile) space of volcanic deposits throughout the volcano’s perimeter presenting a lot of low, rounded and elongated, blister-like mounds. This “blistered terrain” is interpreted to be a subject of “rootless cones,” mounds produced by explosive steam venting or steam swelling when a skinny blanket of scorching volcanic supplies involves relaxation on high of a water or ice-rich floor (Figs. 3 and 6).
Only a yr in the past, Lee, Shubham and their colleague John W. Schutt had recognized the spectacular stays of a glacier — or “relict glacier” — by way of a sizeable erosional opening in the identical volcanic blanket, within the type of a light-toned deposit (LTD) of sulfate salt with the morphologic traits of a glacier. The sulfate deposit, made primarily of jarosite, a hydrous sulfate, was interpreted to have fashioned when the blanket of volcanic pyroclastic supplies got here to relaxation on a glacier and reacted chemically with the ice. Breached rootless cones recognized within the present research present comparable occurrences of polyhydrated sulfates, additional suggesting the burned volcanic blanket could also be hiding an unlimited sheet of glacier ice beneath it (Fig. 6).
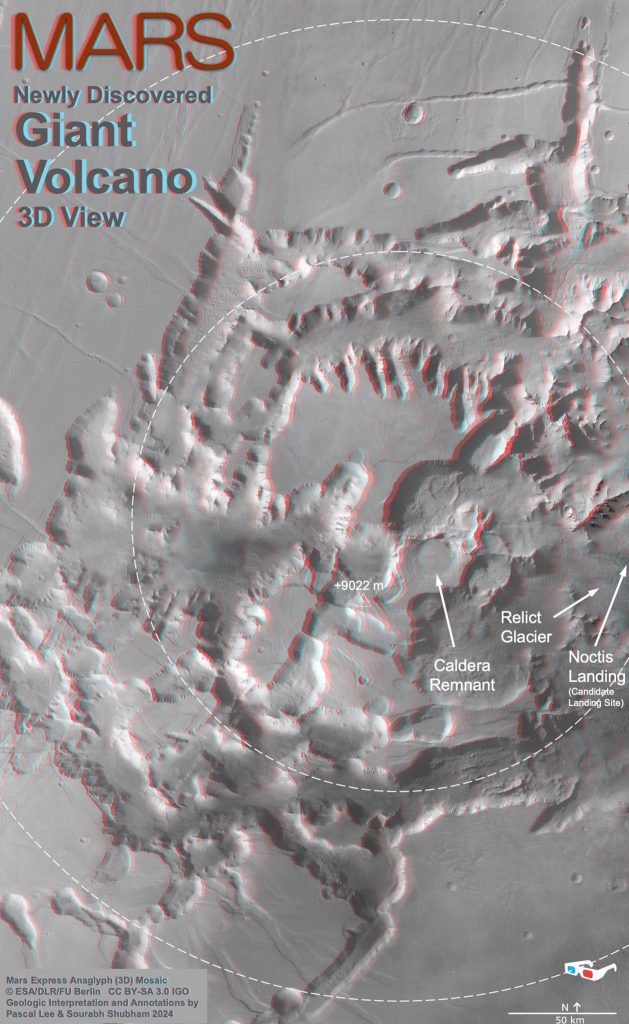
Determine 5: Noctis volcano in 3D.
Anaglyph picture exhibiting parts of the Noctis volcano’s 250 km (155 mile) diameter internal zone of excessive elevation stays, and 450 km (280 mile) diameter outer zone of different stays related to the volcano. Along with the volcano’s summit, caldera remnant, and internal and outer zones, this 3D map reveals the “relict glacier” found in 2023 and Noctis Touchdown, a candidate touchdown website for future robotic and human exploration.
Credit score: Background picture: Mars Categorical anaglyph (3D) mosaic © ESA/DLR/FU Berlin CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO. Geologic interpretation and annotations by Pascal Lee and Sourabh Shubham 2024.
Advanced Historical past and Future Exploration
The Noctis volcano presents an extended and sophisticated historical past of modification, probably from a mixture of fracturing, thermal erosion, and glacial erosion. Researchers interpret the volcano to be an unlimited defend made from layered accumulations of pyroclastic supplies, lavas, and ice, the latter ensuing from repeated buildups of snow and glaciers on its flanks by way of time. As fractures and faults ultimately developed, specifically in reference to the uplift of the broader Tharsis area on which the volcano sits, lavas started to rise by way of completely different components of the volcano, resulting in thermal erosion and elimination of huge quantities of buried ice and the catastrophic collapse of whole sections of the volcano.
Subsequent glaciations continued their erosion, giving many canyons throughout the construction their current distinctive form. On this context the “relict glacier” and the potential buried sheet of glacier ice round it, is likely to be remnants of the newest glaciation episode affecting the Noctis volcano.
However a lot concerning the newly found big volcano stays a thriller. Though it’s clear that it has been lively for a very long time and commenced to construct up early in Mars’ historical past, it’s unknown how early precisely. Equally, though it has skilled eruptions even in trendy occasions, it’s unknown whether it is nonetheless volcanically lively and may erupt once more. And if it has been lively for a really very long time, may the mixture of sustained heat and water from ice have allowed the location to harbor life?
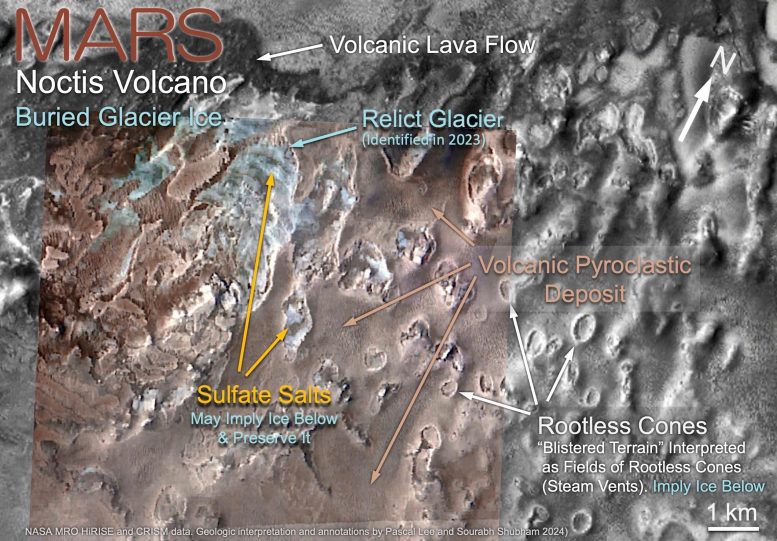
Determine 6: Doable buried glacier ice close to the bottom of the Noctis volcano.
A well-preserved volcanic lava circulation and pyroclastic deposit within the southeastern a part of the Noctis volcano recommend that the volcano remained lively even in comparatively latest occasions. The pyroclastic deposit presents “blisters” at its floor, interpreted as “rootless cones” or steam vents produced when the recent pyroclastic supplies got here in touch with H2O ice. Breaches within the pyroclastic deposit reveal light-toned deposits (LTDs) of sulfate salts, anticipated merchandise of chemical reactions between pyroclastic supplies and H2O ice. The most important LTD of sulfates on this space had already been described as a “relict glacier,” because it presents a variety of morphologic traits particular to glaciers, suggesting that glacier ice may nonetheless be preserved, solely protected beneath a skinny layer of sulfate salts. By extension, the rootless cones and different sulfate deposits on this space could also be blanketing much more glacier ice.
Credit score: Background pictures: NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) Excessive Decision Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE), Context Imager (CTX), and Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM). Geologic interpretation and annotations by Pascal Lee and Sourabh Shubham 2024.
As mysteries surrounding the Noctis volcano proceed to puzzle scientists, the location is already rising as an thrilling new location to check Mars’ geologic evolution, seek for life, and plan future robotic and human exploration. The potential presence of glacier ice at shallow depths close to the equator signifies that people may doubtlessly discover a much less frigid a part of the planet whereas nonetheless having the ability to extract water for hydration and manufacturing rocket gas (by breaking down H2O into hydrogen and oxygen).
“It’s actually a mixture of issues that makes the Noctis volcano website exceptionally thrilling. It’s an historic and long-lived volcano so deeply eroded that you would hike, drive, or fly by way of it to look at, pattern, and date completely different components of its inside to check Mars’ evolution by way of time. It has additionally had an extended historical past of warmth interacting with water and ice, which makes it a major location for astrobiology and our seek for indicators of life. Lastly, with glacier ice doubtless nonetheless preserved close to the floor in a comparatively heat equatorial area on Mars, the place is wanting very enticing for robotic and human exploration,” mentioned Lee.
This research was performed utilizing information from NASA’s Mariner 9, Viking Orbiter 1 and a pair of, Mars World Surveyor, Mars Odyssey, and Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter missions, in addition to ESA’s Mars Categorical mission. Particular appreciation is expressed to their instrument groups for buying the varied datasets used on this research. Use of the open NASA Planetary Knowledge System, Mars Quickmap, Mars Trek, and Google Mars on-line information visualization instruments was additionally key in enabling the research.
Reference: “Massive Eroded Volcano Advanced and Buried Glacier Ice in Jap Noctis Labyrinthus: Proof for Current Volcanism and Glaciation Close to Mars’ Equator” by Pascal Lee and Sourabh Shubham, fifty fifth Lunar and Planetary Science Convention.
PDF
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

