[ad_1]
Notice to the reader: That is the eleventh in a sequence of articles I am publishing right here taken from my e-book, “Investing with the Development.” Hopefully, you will see this content material helpful. Market myths are usually perpetuated by repetition, deceptive symbolic connections, and the whole ignorance of info. The world of finance is filled with such tendencies, and right here, you will see some examples. Please needless to say not all of those examples are completely deceptive — they’re generally legitimate — however have too many holes in them to be worthwhile as funding ideas. And never all are instantly associated to investing and finance. Get pleasure from! – Greg
Market Valuations
As a result of secular markets are outlined by long-term swings in valuations, let’s take a look at the Worth Earnings (PE) ratio and research its historical past. Robert Shiller created a invaluable measure of PE valuation that makes use of trailing (precise) earnings, averaged over a 10-year interval. This is how it’s calculated:
- Use the yearly incomes of the S&P 500 for every of the previous 10 years.
- Modify these earnings for inflation, utilizing the CPI (i.e. quote every earnings determine in present {dollars}).
- Common these values (i.e., add them up and divide by 10), giving us e10.
- Take the present Worth of the S&P 500 and divide by e10.
Determine 8.1 reveals the S&P Composite on a month-to-month foundation adjusted for inflation, again to 1871, with a regression line so you will get a really feel (visually) of the place the present worth is relative to the long-term development of costs. The decrease plot is the Shiller PE10 plot, with peaks and troughs recognized with their values. You may see that every one prior secular bears ended with PE10 as a single digit (4.8, 5.6, 9.1, and 6.6). The PE10, on March 9, 2009, solely bought all the way down to 13.3, which is significantly increased than the extent reached by all prior secular bear lows. Primarily based on this straightforward analogy, I believe we’ve but to see the secular bear low for this cycle. Keep in mind, it doesn’t imply that the costs should go decrease than they did in 2009; it simply means the PE10 ought to drop to single digits. Keep in mind, PE is a ratio of Worth over Earnings. To make the ratio smaller, both the worth can decline, the earnings can enhance, or a mix of each.
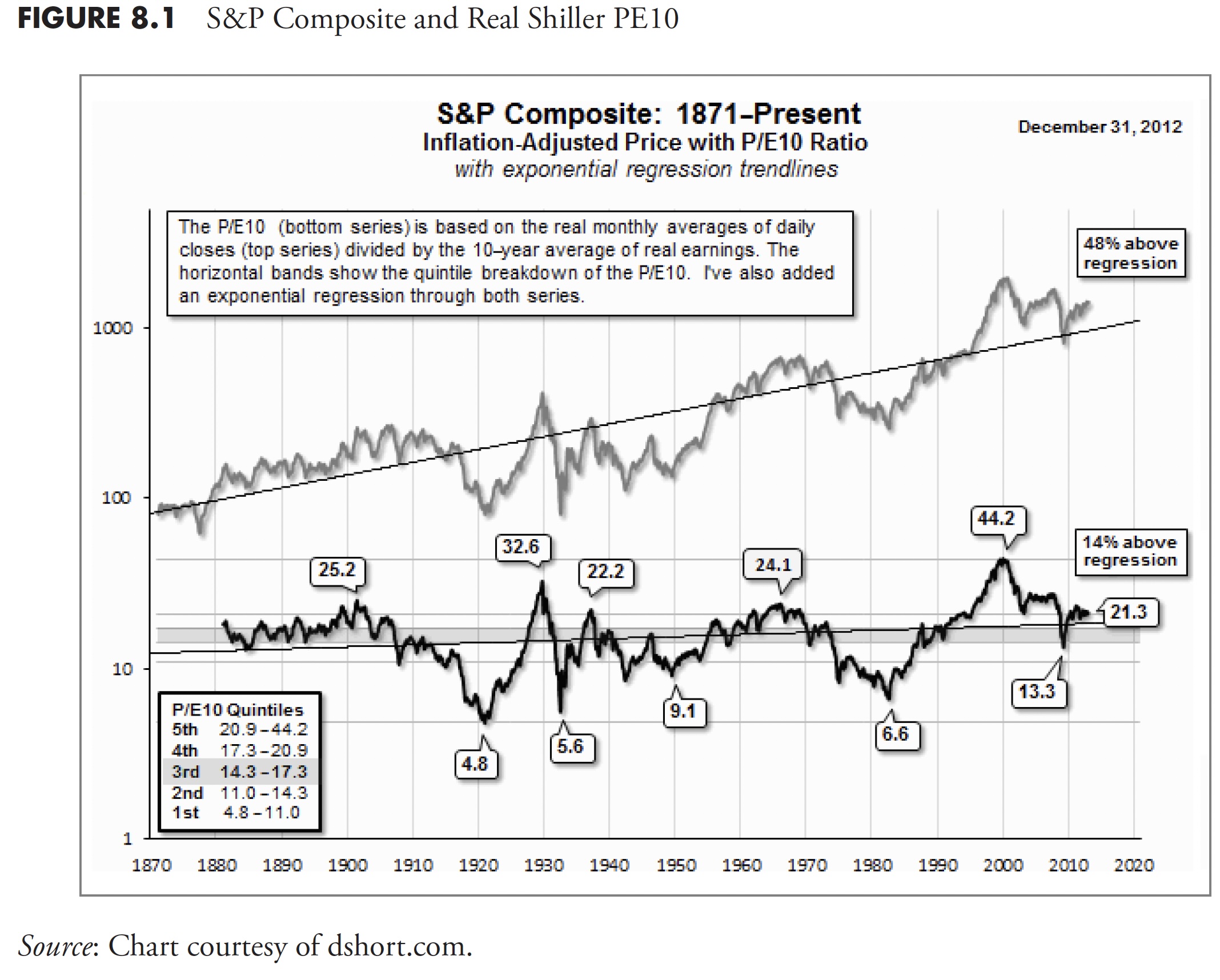
As of December 31, 2012, the PE10 is at 21.3. Referencing the small field within the decrease left nook reveals that this worth is within the fifth quintile of all of the PE knowledge. Primarily based on this evaluation, the market is overvalued.
So when the monetary information noise is consistently parading analysts by touting the PE as overvalued or undervalued, you’ll be able to depend on the truth that they’re utilizing the ahead PE ratio. The ahead ratio is the guess of all of the earnings analysts. They’re hardly ever right. Ignore them.
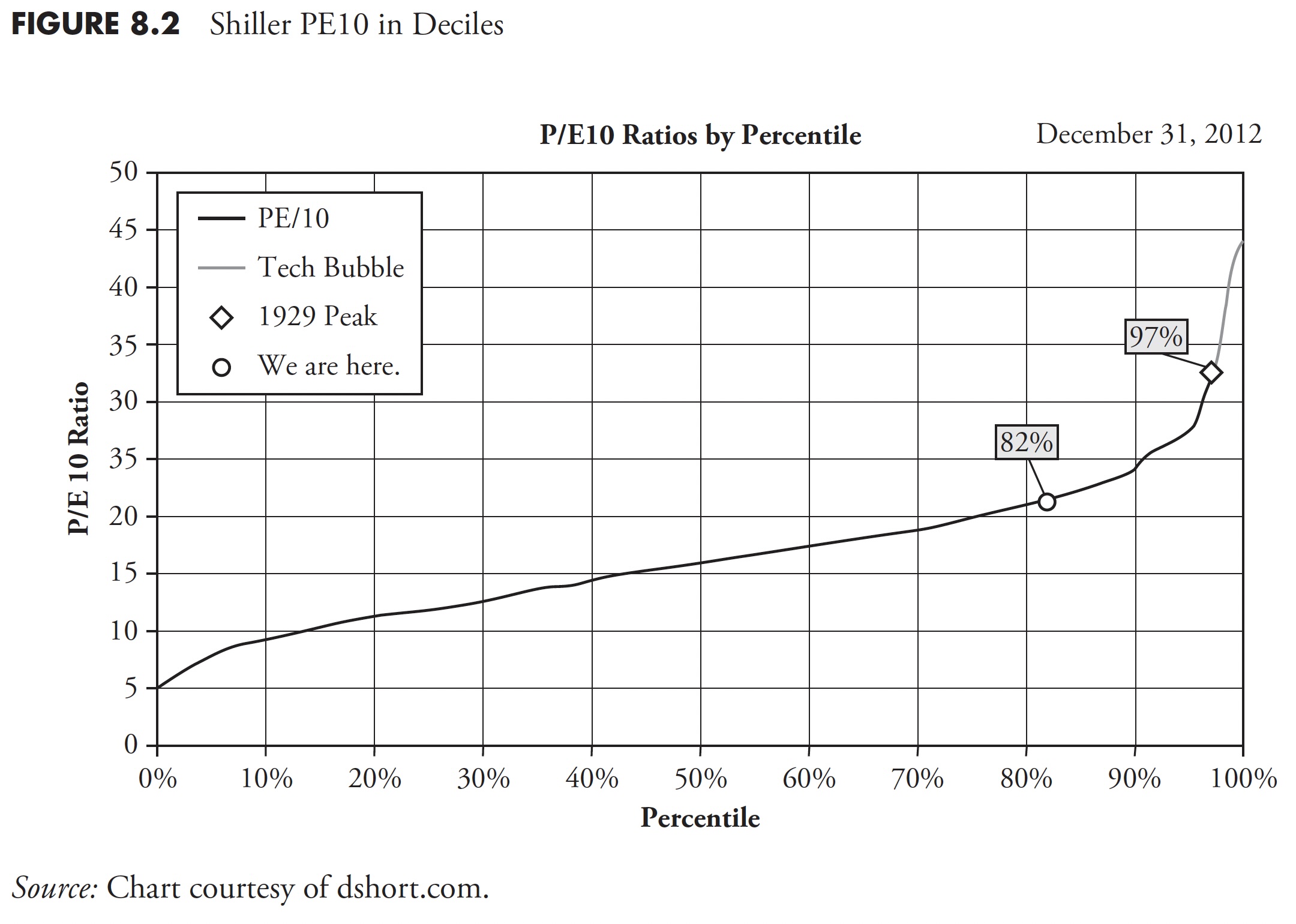
Lastly, Determine 8.2 reveals the PE10 in 10 % increments or deciles. It reveals the acute stage reached within the late Nineties from the tech bubble, it reveals the 1929 peak, and it reveals that, as of December 31, 2012, we’re on the 82nd percentile of PE10. This places the PE10 overvalued on a relative foundation, and in addition on an absolute foundation, as proven in Determine 8.1. Keep in mind, PE10 used actual reported (trailing) earnings, not ahead (guess) earnings. As Doug Quick says on his web site at dshort.com: A extra cautionary commentary is that when the PE10 has fallen from the highest to the second quintile, it has finally declined to the primary quintile and bottomed in single digits. Primarily based on the newest 10-year earnings common, to succeed in a PE10 within the excessive single digits would require an S&P 500 worth decline under 540. After all, a happier different could be for company earnings to proceed their sturdy and extended surge. If the 2009 trough was not a PE10 backside, when would we see it happen? These secular declines have ranged in size from greater than 19 years to as few as three. As of December 31, 2012, the decline in valuations was approaching its thirteenth 12 months.
Secular Bear Valuation
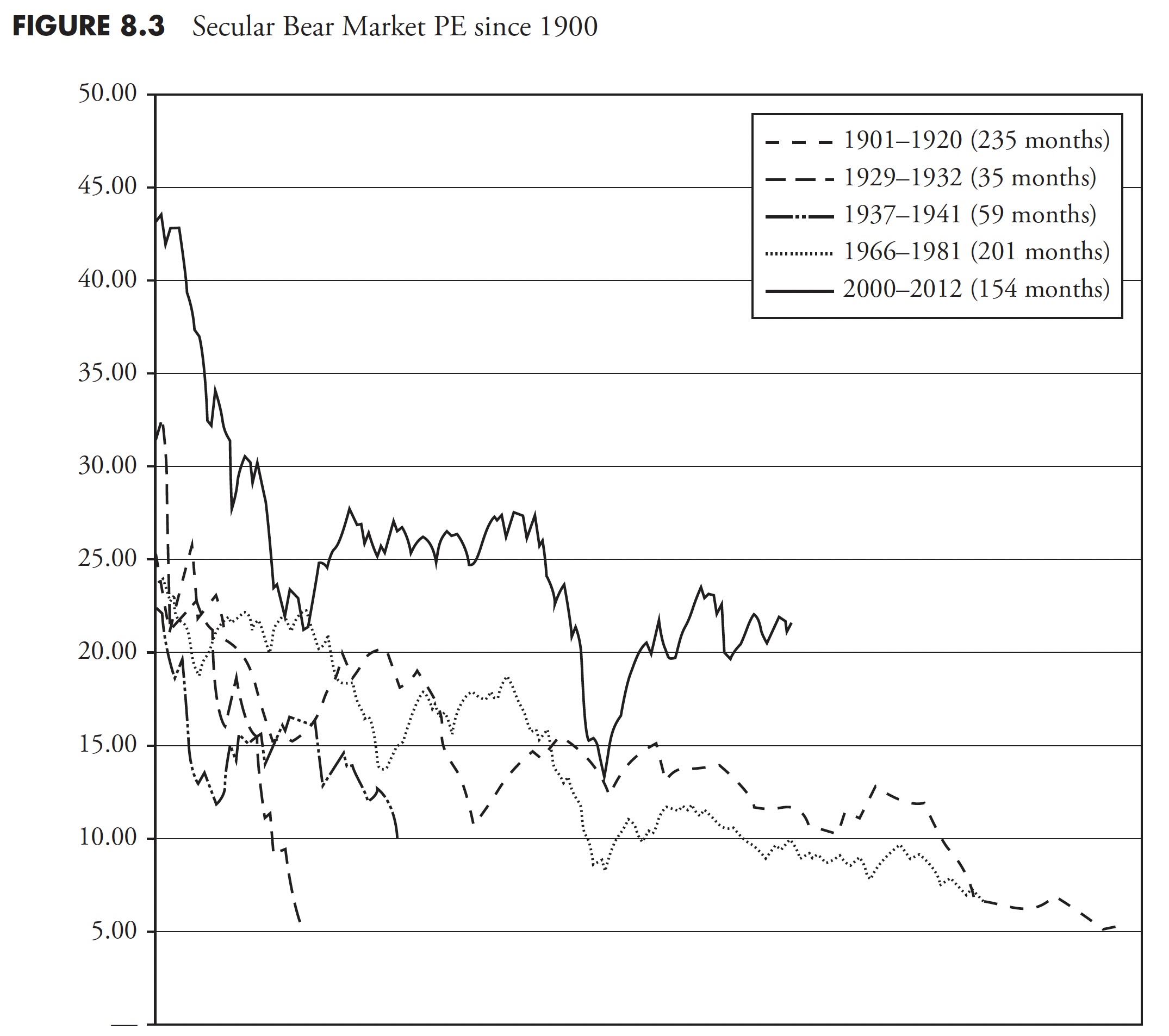
Determine 8.3 reveals the Shiller PE10 month-to-month for all of the previous secular bear markets since 1900, with the present secular bear (as of 2013) in daring. What is basically attention-grabbing about this chart is that many of the secular bears started with PE Ratios within the 20 to 30 vary and ended with them within the 5 to 10 vary. The present secular bear started with a PE within the mid-40s and is now solely again all the way down to the extent that the earlier secular bears started. That would indicate that the secular bear that started in 2000 could possibly be a protracted one. These charts had been created utilizing month-to-month knowledge; if yearly knowledge had been used, the idea could be much more pronounced.
Secular Bear Valuation Composite
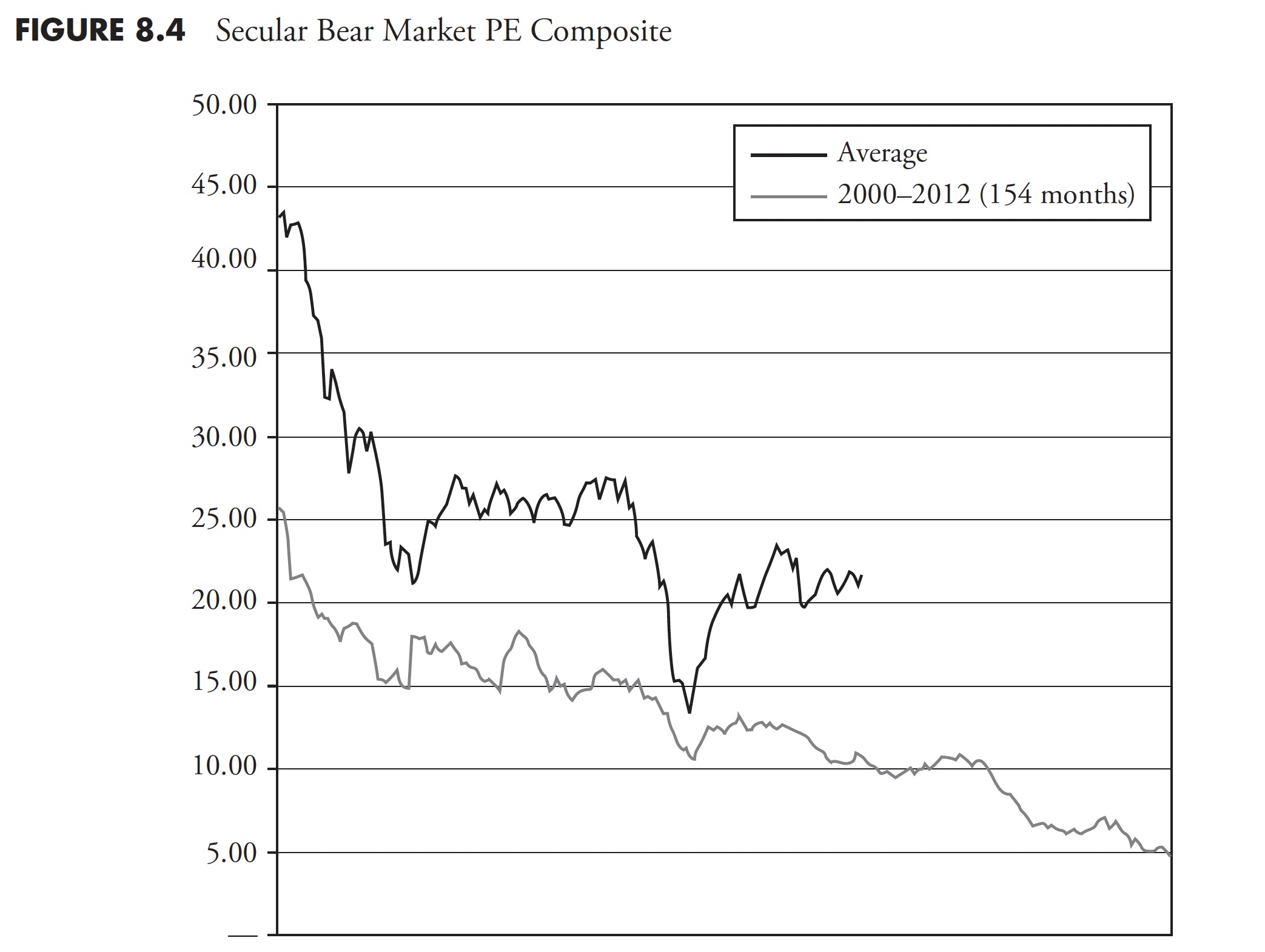
In Determine 8.4, the present secular bear market valuation is proven in daring, with the opposite line representing the typical of the earlier 4 secular bears. Once more, any such evaluation is simply an commentary and for academic functions; you can not make funding choices from this. Funding choices come from actionable data and evaluation.
Secular Bull Valuation
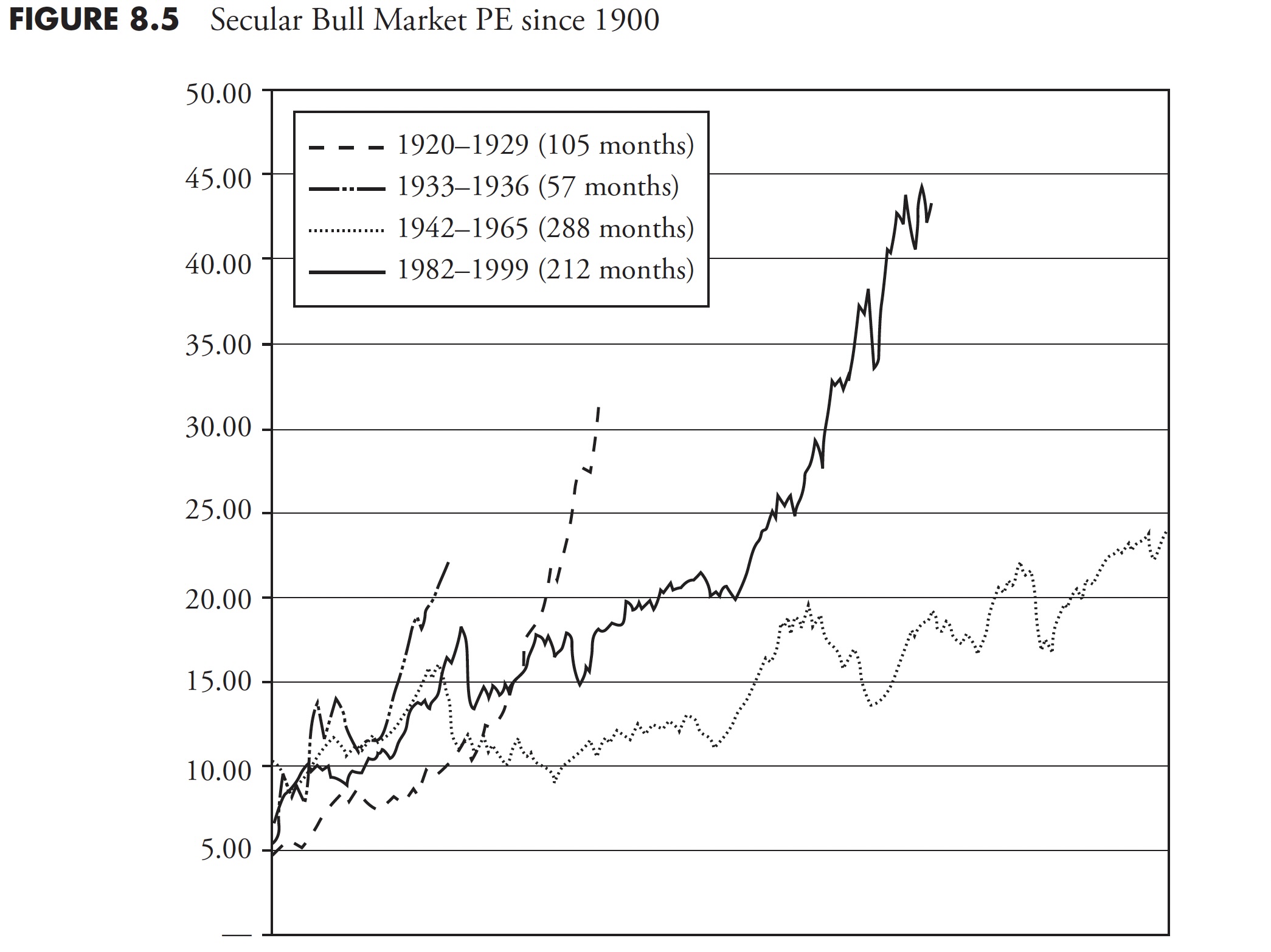
Determine 8.5 of secular bull market valuations reveals that almost all of them start with PE ratios within the 5 to 10 (similar as the place secular bears finish) and so they finish with PE ratios within the 20 to 30 vary. The extreme secular bull of 1982 to 2000 reached unbelievable excessive valuations. I bear in mind everybody saying that this time was totally different. Improper!
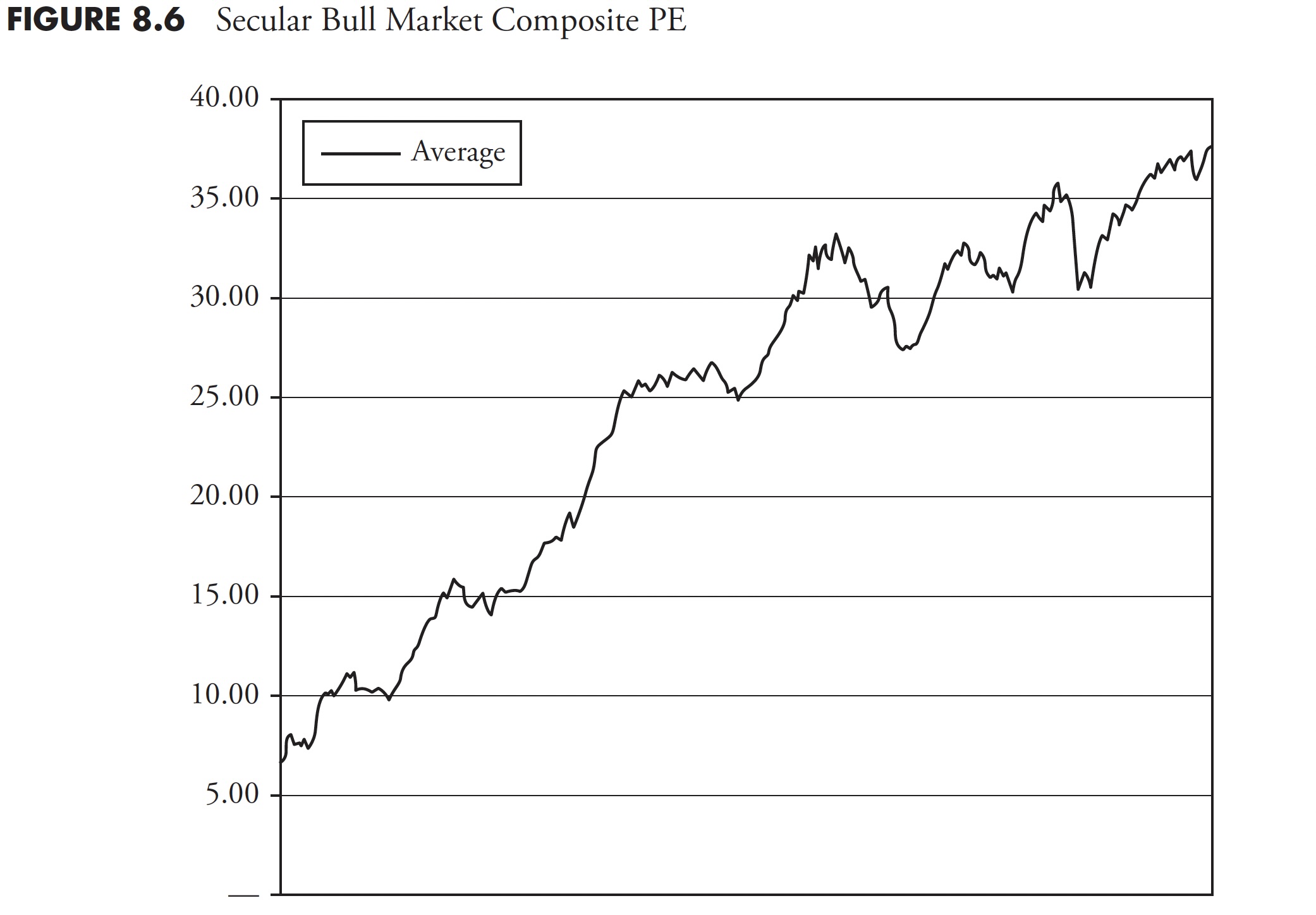
Secular Bull Valuation Composite
The secular bull market valuation composite is proven in Determine 8.6. It’s the common of all of the secular bull markets since 1900. Since we’re presently in a secular bear market, the typical of the secular bull markets is proven by itself.
Market Sectors
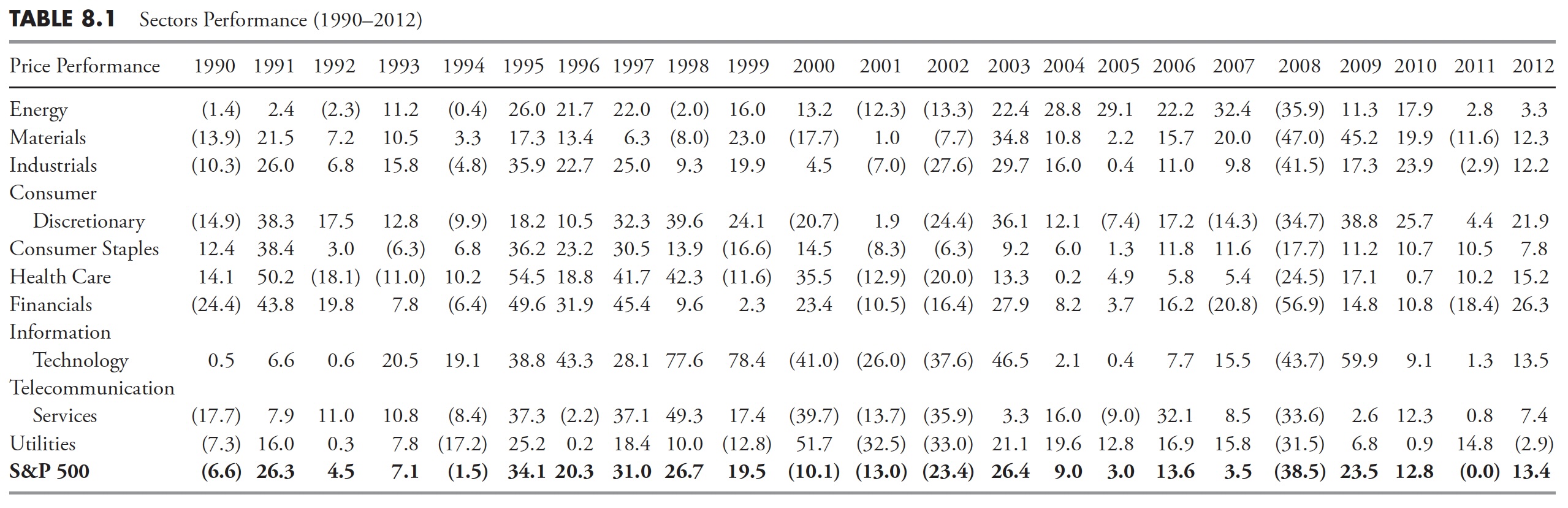
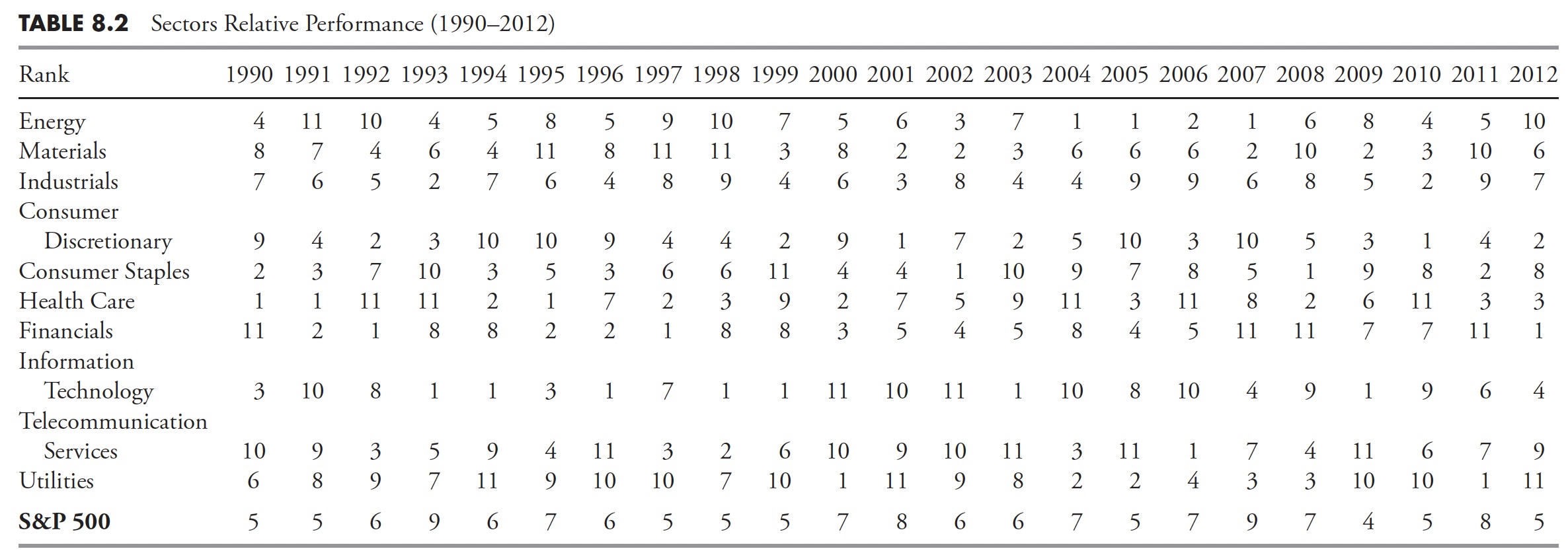
I exploit the sector definitions supplied by Normal & Poor’s, of which there are 10. The opposite major supply for sector evaluation is Dow Jones. Both is okay, I simply choose the S&P construction as a result of I’ve been utilizing it for thus lengthy. Desk 8.1 reveals the ten sectors’ annual worth efficiency since 1990, and Desk 8.2 reveals the relative efficiency of the full returns. When viewing a desk of relative returns as in Desk 8.2, needless to say every column (12 months) is totally unbiased of the previous 12 months or following 12 months. Additionally, the relative rating reveals that these within the high a part of the column outperformed these within the decrease a part of the column, unbiased of whether or not the returns had been optimistic, damaging, or a mix. One other worth of any such desk is to point out that choosing final 12 months’s high performer isn’t a very good technique. Keep in mind, you can not retire on relative returns.
This e-book doesn’t get into the varied makes use of of sectors as investments, however the e-book wouldn’t be full with out the point out of sector rotation and, specifically, how varied sectors rotate out and in of favor based mostly on the section of the enterprise cycle and the economic system. An additional delineation of sectors is their propensity to fall inside the broad classes of offensive and defensive. Because of this when the market is performing poorly, the defensive sectors will usually outperform, and when the market is performing effectively, it’s the offensive sectors which might be the highest performers.
The phases of the economic system generally known as financial expansions and contractions are affected by many occasions however usually boil all the way down to recessions and durations of growth. It must be famous, nonetheless, that not all contractions find yourself being recessions. The phases can then be damaged down into early cycle, mid-cycle, and late cycle segments of the complete cycle. There’s loads of literature obtainable to cowl all these particulars, however the level of this dialogue is to point out the rotational motion of the varied sectors by means of the financial cycle.
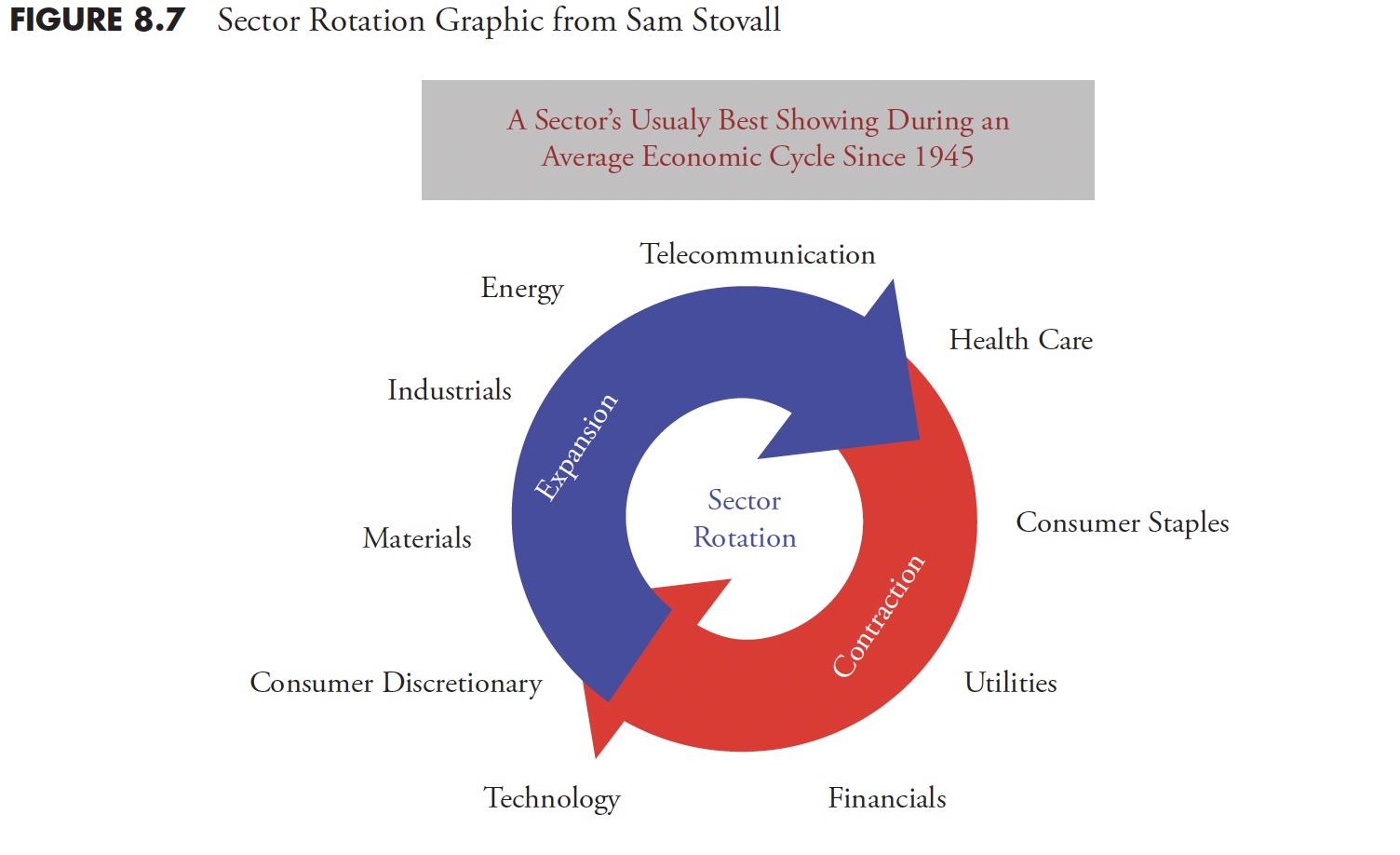
Determine 8.7 is a graphic displaying the sectors and the place they fall within the cycle. It reveals the rotation of sectors throughout a mean financial cycle for the previous 67 years and is courtesy of Sam Stovall, chief fairness strategist, S&P Capital IQ. Sam wrote the most effective books on sector rotation years in the past, Normal & Poor’s Sector Investing: Tips on how to Purchase the Proper Inventory within the Proper Business at The Proper Time, however is presently out of print as of 2013.
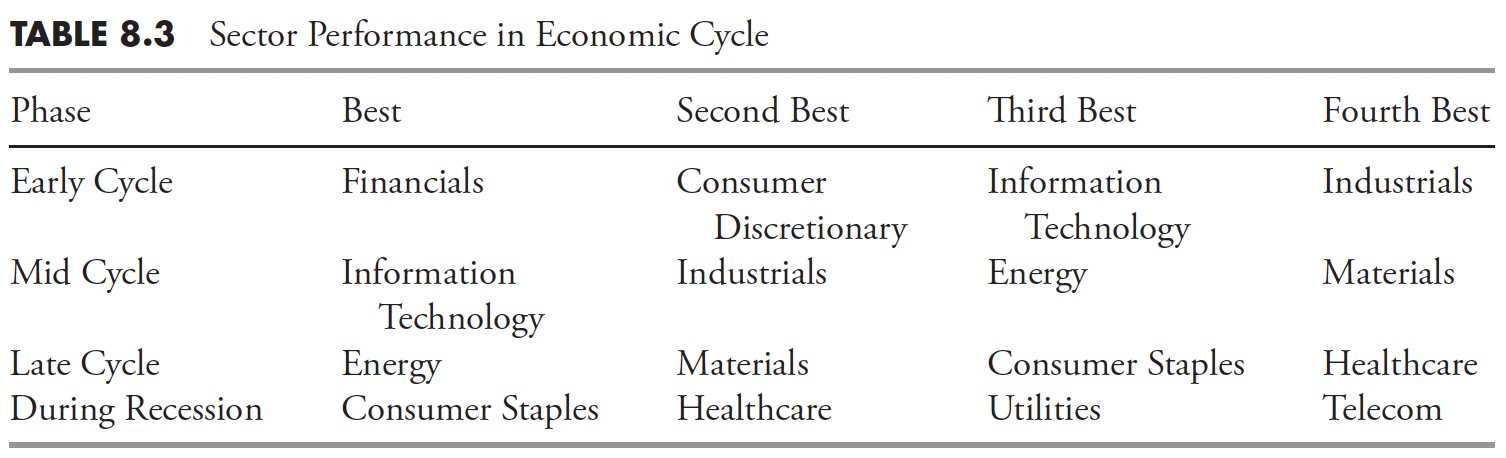
One other glorious research I’ve seen on the cycles inside the phases and what sectors are affected was put out by Constancy and dated August 23, 2010 (see Desk 8.3). It clearly confirmed that, from 1963 by means of 2010, the next sectors had been strongest in the course of the varied phases. In every cycle, the top-performing sectors are proven, with the primary being the very best of the 4 and the final being the worst of the highest 4, which remains to be the fourth finest out of the ten sectors.
It was attention-grabbing to notice on this research that in all the three cycles, Utilities and Healthcare had been the 2 worst-performing of all 10 of the sectors (not proven). They solely ranked within the high 4 throughout precise recessions. Since recessions are normally recognized by the NBER a couple of 12 months after they start and someday not till they’ve ended, this isn’t information you could make funding choices with.
Nonetheless, you should utilize a momentum evaluation and all the time be within the high 4 sectors and possibly do effectively. Clearly, that is definitely higher than buy-and-hold or index investing.
Determine 8.8 reveals the S&P 500 within the high plot and my Offensive-Defensive Measure within the decrease plot. The idea of the Offensive-Defensive Measure is straightforward.
The Offensive Elements
- Client Discretionary
- Financials
- Industrials
- Data Expertise
The Defensive Elements
- Client Staples
- Utilities
- Healthcare
- Telecom
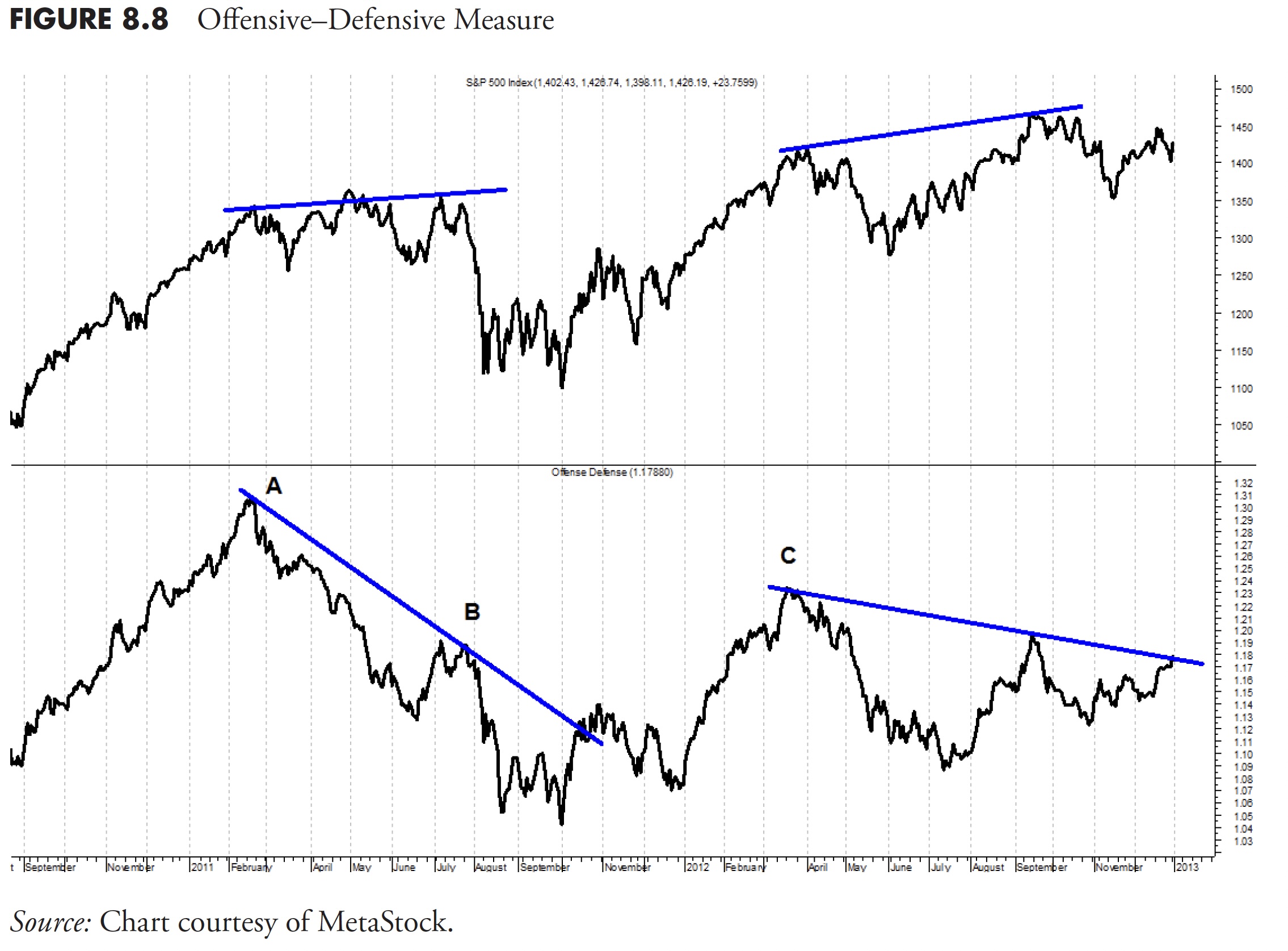
You may see that the rally from the left facet of the chart to level A (February, 2011) was sturdy; nonetheless, based mostly on the swap from offensive to defensive sectors that occurred at level A, the traders had been clearly involved in regards to the market. Whereas the market traded sideways for months (see high plot), the defensive sectors had been clearly within the lead, inflicting the offense-defense measure to say no. The measure declined considerably, and it wasn’t till level B (July 2011) that the market lastly gave up and headed south.
Sector Rotation in 3D
Julius de Kempenaer has created a novel approach of visualizing sector-rotation, or, extra usually, “market-rotation,” in such a approach that the relative place of all parts in a universe (sectors, asset courses, particular person equities, and many others.) might be analyzed in a single single graph as a substitute of getting to flick through all potential combos. This graphical illustration known as a Relative Rotation Graph or RRG. As of 2013, Julius is now working along with Trevor Neil to additional analysis and implement using RRGs within the funding strategy of funding firms, funds, and particular person traders. Extra data might be discovered on their web site www.relativerotationgraphs.com.
A Relative Rotation Graph takes two inputs that collectively mix into an RRG. I will use the S&P Sectors for this dialogue. Step one is to provide you with a measure of relative power of a sector versus the S&P 500; that is performed by taking a ratio between every sector and the S&P 500. Analyzing the slope and tempo of those particular person RS traces offers a fairly good clue about particular person comparisons versus their benchmark. These uncooked RS traces reply “good” or “dangerous.” Nonetheless, they don’t reply “how good” or “how dangerous” or “finest” and “worst.” The explanation for that is that Uncooked RS values (sector/benchmark) for the varied parts within the universe are like apples and oranges, as they can’t be in contrast based mostly on their numerical worth.
Taking the relative positions of all parts in a universe under consideration in a uniform approach allows “rating.” This course of normalizes the varied ratios in such a approach that their values might be in contrast as apples to apples, not solely towards the benchmark but additionally towards one another. The ensuing numerical worth is called the JdK RS-Ratio—the upper the worth, the higher the relative power. Moreover, not solely the extent of the ratio, but additionally the course and the tempo at which it’s transferring, impacts the end result. An idea much like the well-known MACD indicator is used to measure the Charge of Change or Momentum of the JdK RS-Ratio line. Right here additionally, you will need to preserve comparable values so one other normalization algorithm is utilized to the ROC; this line is called the JdK RS-Momentum. The RRG now has JdK RS-Ratio for the abscissa (X axis) and the JdK RS-Momentum for the ordinate (Y axis). Graphically, the rotation seems like Determine 8.9.
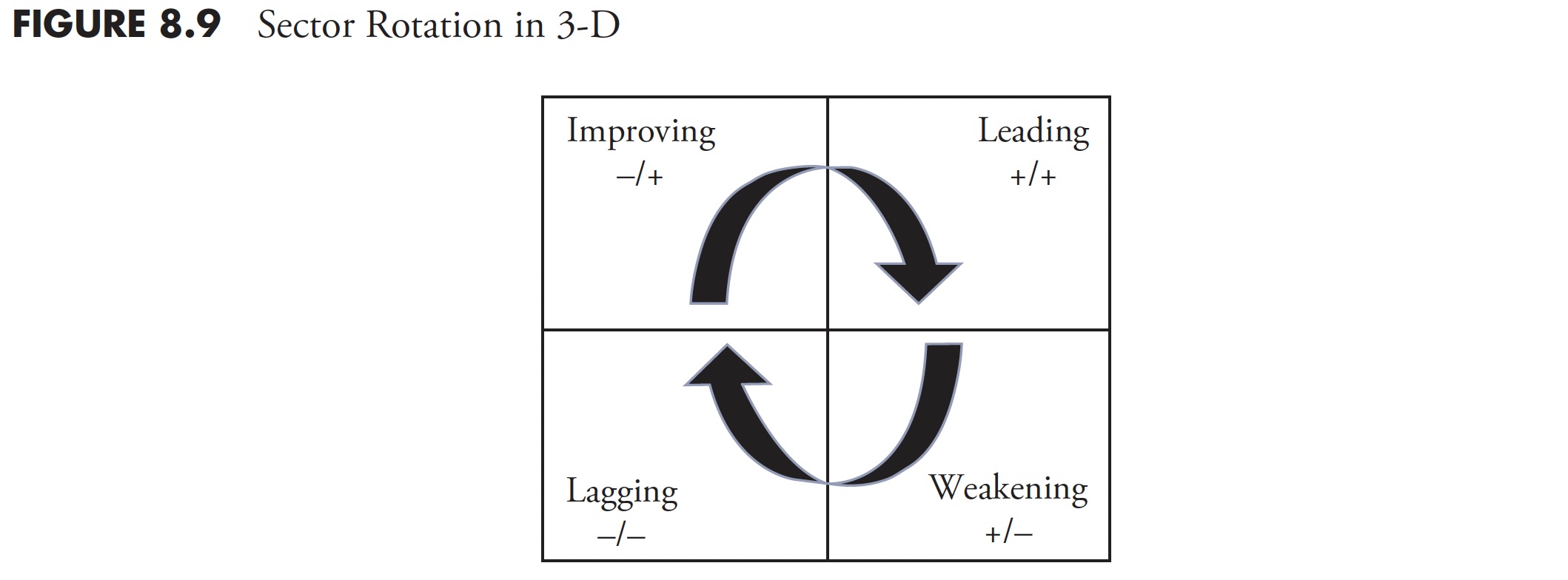
In Determine 8.10, the sectors which might be displaying sturdy relative power, which remains to be being pushed increased by sturdy momentum, will present up within the top-right quadrant. By default, the Charge of Change will begin to flatten first, then start to maneuver down. When that occurs, the sector strikes into the bottom-right quadrant. Right here, we discover the sectors which might be nonetheless displaying optimistic relative power, however with declining momentum. If this deterioration continues, the sector will transfer into the bottom-left quadrant. These are the sectors with damaging relative power, which is being pushed farther down by damaging momentum. As soon as once more, by default, the JdK RS-Momentum worth will begin to transfer up first, which is able to push the sector into the top-left quadrant. This the place relative power remains to be weak (i.e. < 100 on the JdK RS-Ratio axis) however its momentum is transferring up. Lastly, if the power persists, the sector can be pushed into the top-right quadrant once more, finishing a full rotation.
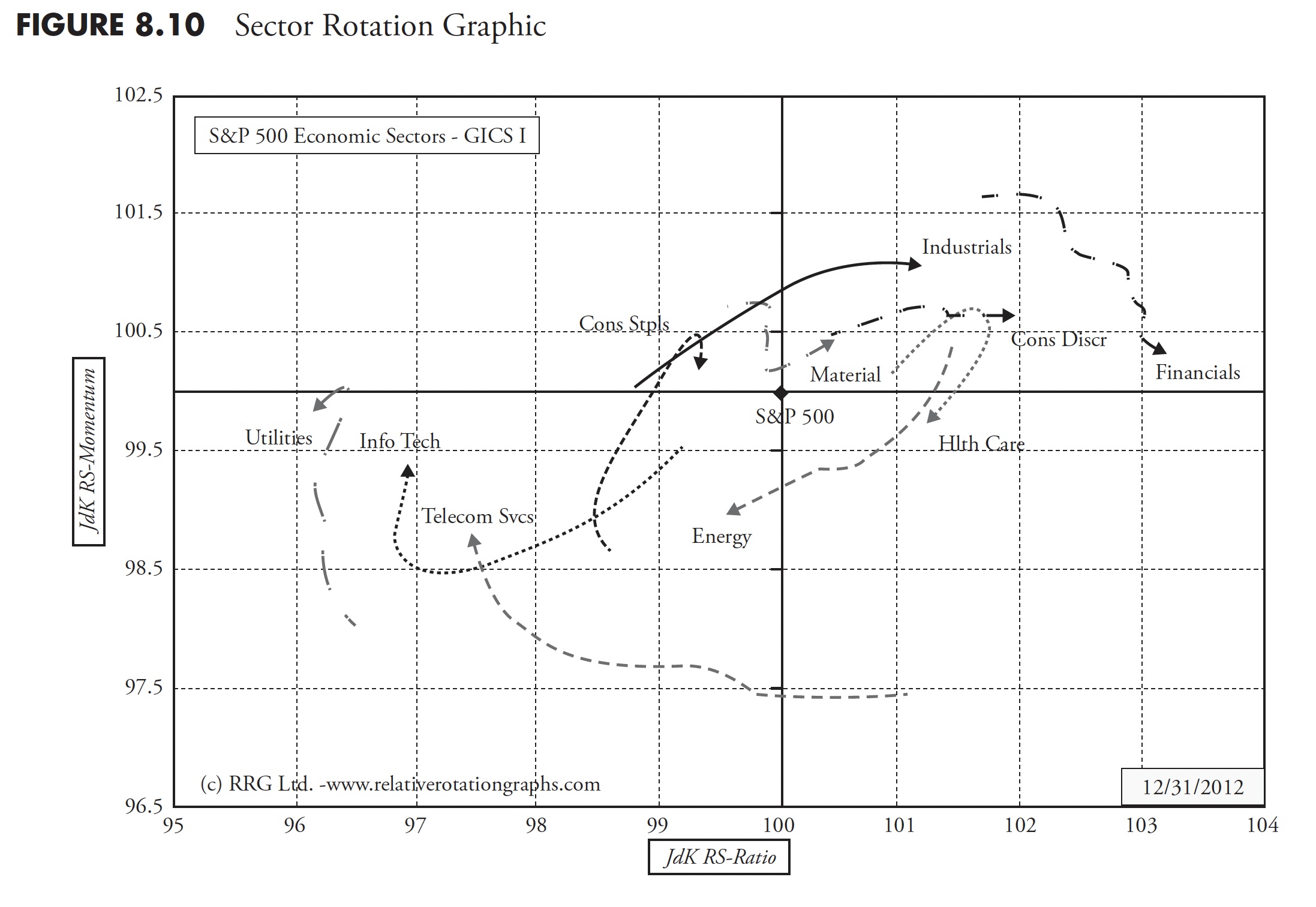
The following step is so as to add the third dimension, time, to the plot to visualise the info on a periodic foundation and in reality, considerably like watching a flip chart or animation in which you’ll be able to see the motion of every of the sectors across the chart as proven in Determine 8.10.
This know-how, in static kind, is obtainable on the Bloomberg skilled service since January 2011 as a local operate (RRG<GO>) the place customers can set their desired universes, benchmarks, lookback durations, and so forth. On their aforementioned web site, Julius and Trevor preserve plenty of RRGs, static and dynamic (animated rotation), on fashionable universes just like the S&P 500 sectors (GICS I & II). A number of skilled in addition to retail software program distributors and web sites are working to embed the RRG know-how of their merchandise, which ought to make this distinctive visualization instrument obtainable to a wider viewers.
Asset Lessons
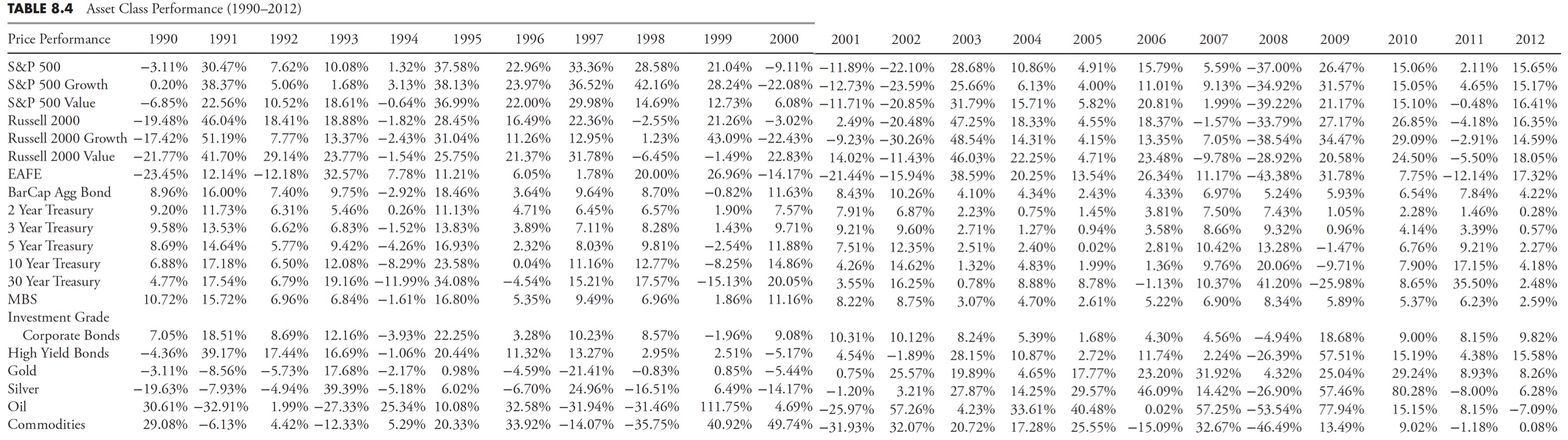
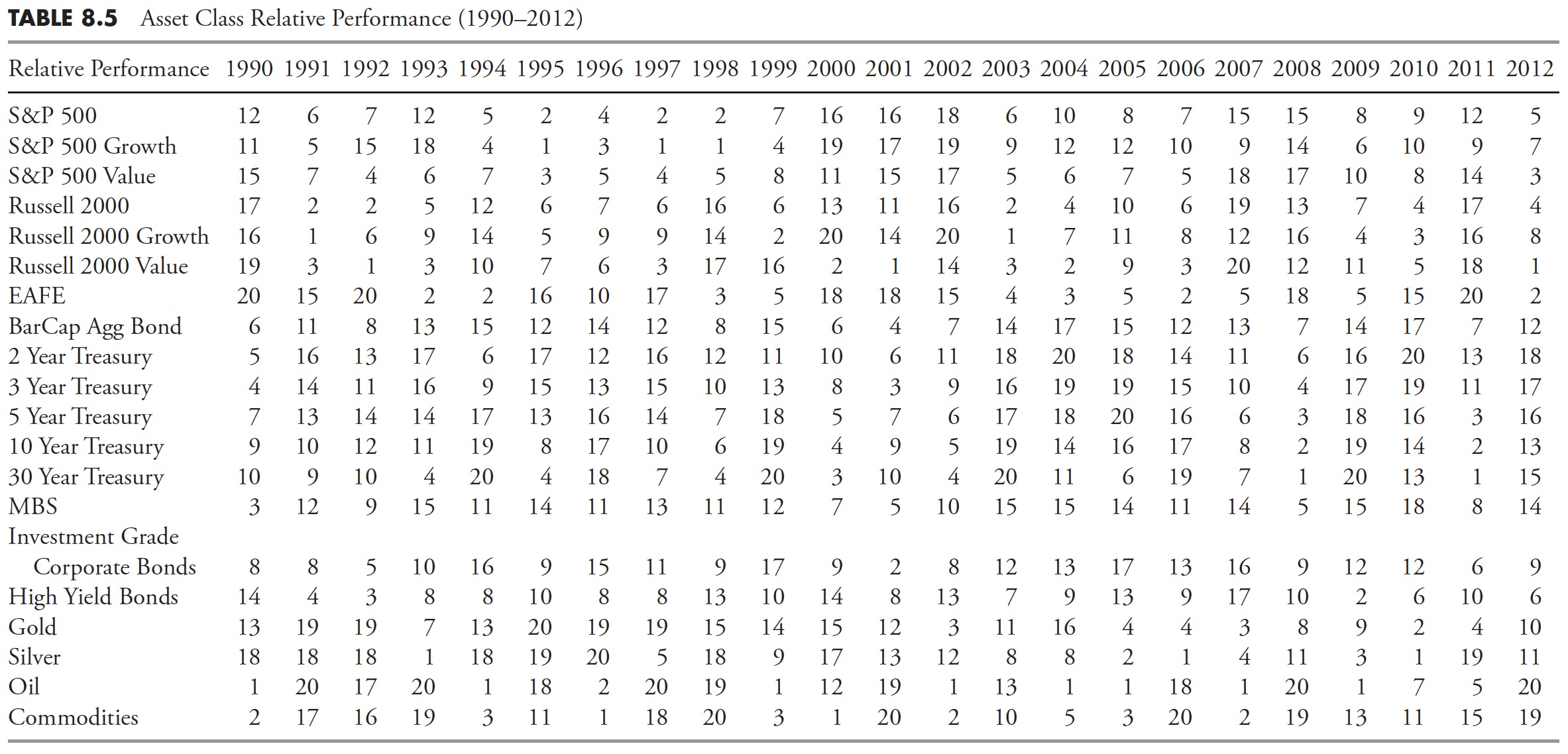
Asset courses might be analyzed precisely the identical as market sectors. The one limitation is that they aren’t tied as intently to financial cycles as sectors, so it’s harder to determine these which might be offensive or defensive. Desk 8.4 reveals the worth efficiency of a mess of asset courses. Keep in mind, this desk is just displaying the annual efficiency of every asset for annually since 1990, whereas Desk 8.5 has the asset courses ranked annually numerically. Usually, any such desk is proven with a number of colours, however considerably troublesome in a black-and-white e-book, so rankings are proven. Once more, keep in mind that the rankings solely present the relative efficiency, and annually is completely unbiased of the previous or following 12 months.
The Misplaced Decade
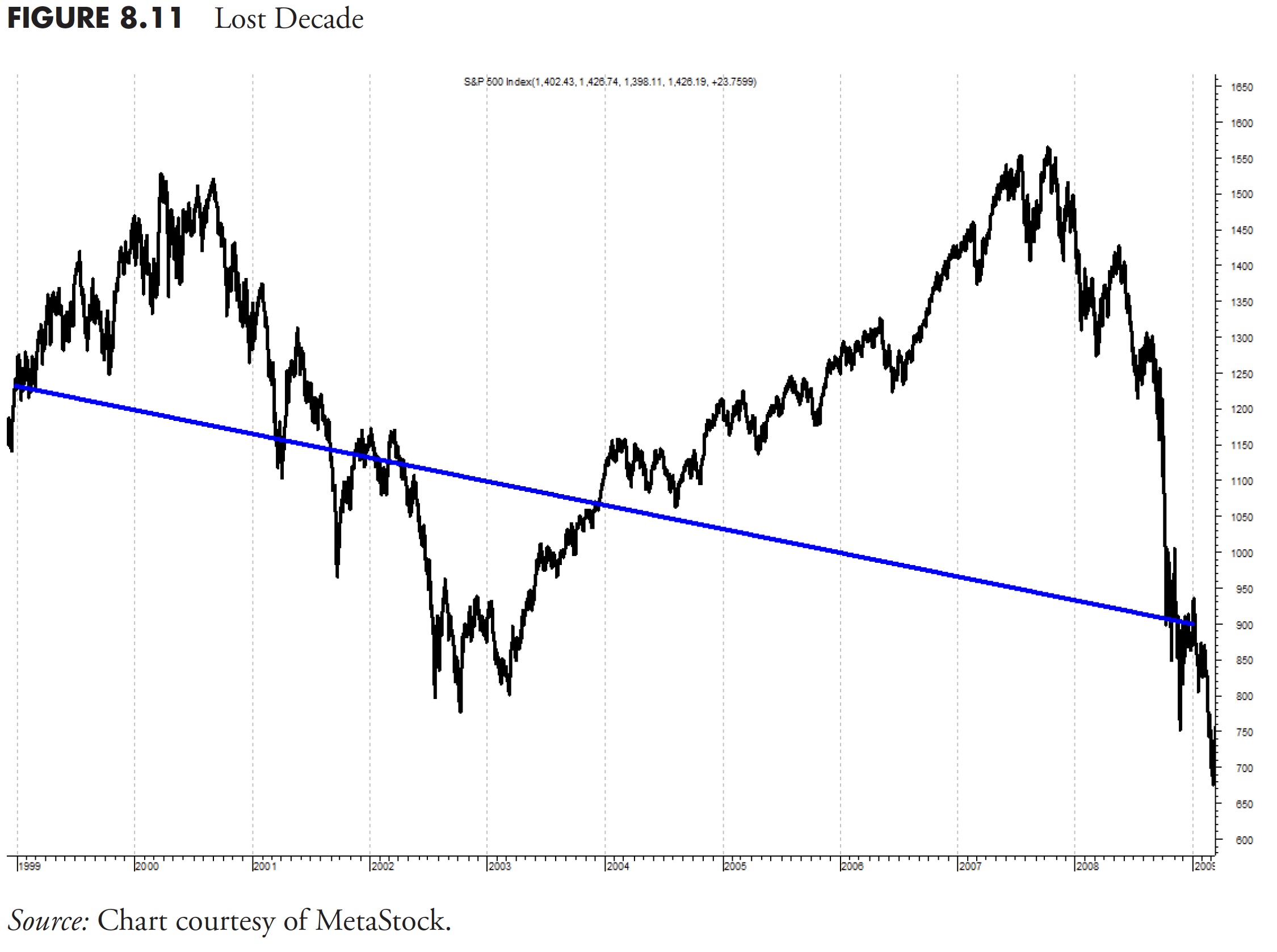
Determine 8.11 reveals the S&P 500 Complete Return from December 31, 1998, to December 31, 2008. Two big bear markets and two good bull markets. When you have a technique that might seize a very good portion of these bull markets and keep away from a very good portion of these bear markets, you’ll do rather well. Purchase and maintain has misplaced cash over this era.
I get requested on a regular basis, “Are we going to have one other bear market?” I reply that I can assure you that we’ll; I simply don’t know when it will likely be. Nonetheless, we are able to flip to a different group of very shiny folks from the third-largest economic system on this planet (as of 2013) and take a look at their market. Determine 8.12 is the Japanese Nikkei from December 31, 1985, to December 31, 2011, a time period of 26 years, over 1 / 4 of a century.
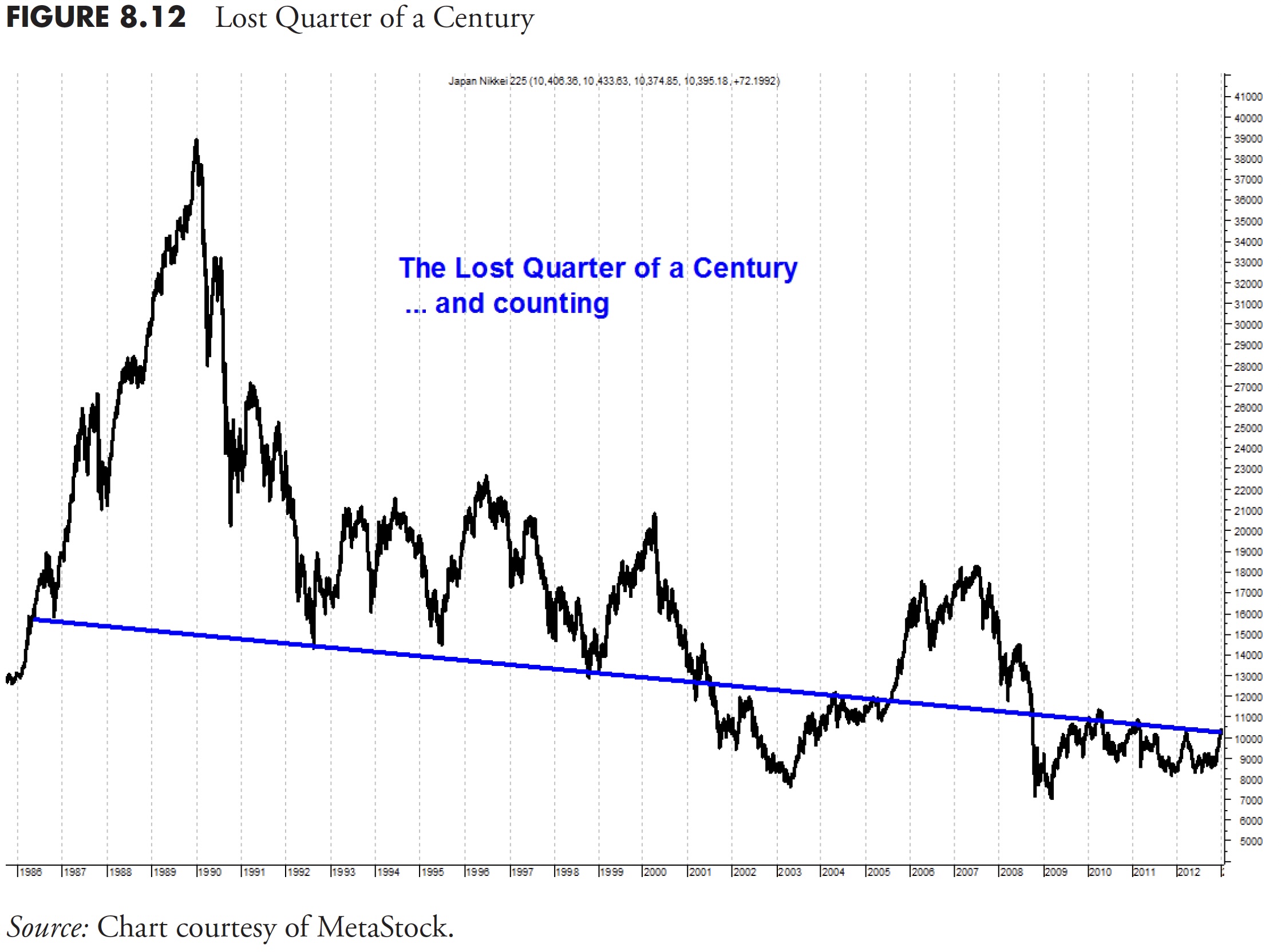
Clearly, purchase and maintain was a devastating funding technique, and the actually dangerous information is that it nonetheless is. Determine 8.13 reveals the up and down strikes throughout this era, during which a very good development following technique might have protected you from horrible devastation.
The share strikes up are proven above the plot, and the proportion strikes down are under the plot. These are the proportion strikes for every of the up and downs you see on the chart. There have been 5 cyclical bull strikes of larger than 60 % throughout this era. There have been additionally 5 cyclical bear strikes of larger than -40 %. Keep in mind, a 40 % loss requires a achieve of 66 % simply to get again to even. The small field within the decrease proper edge reveals the decline from the market high in late December 1989 (–73.3 %). A 73 % decline requires a achieve of 285 % to get again even. Most individuals will not stay lengthy sufficient for that to occur.
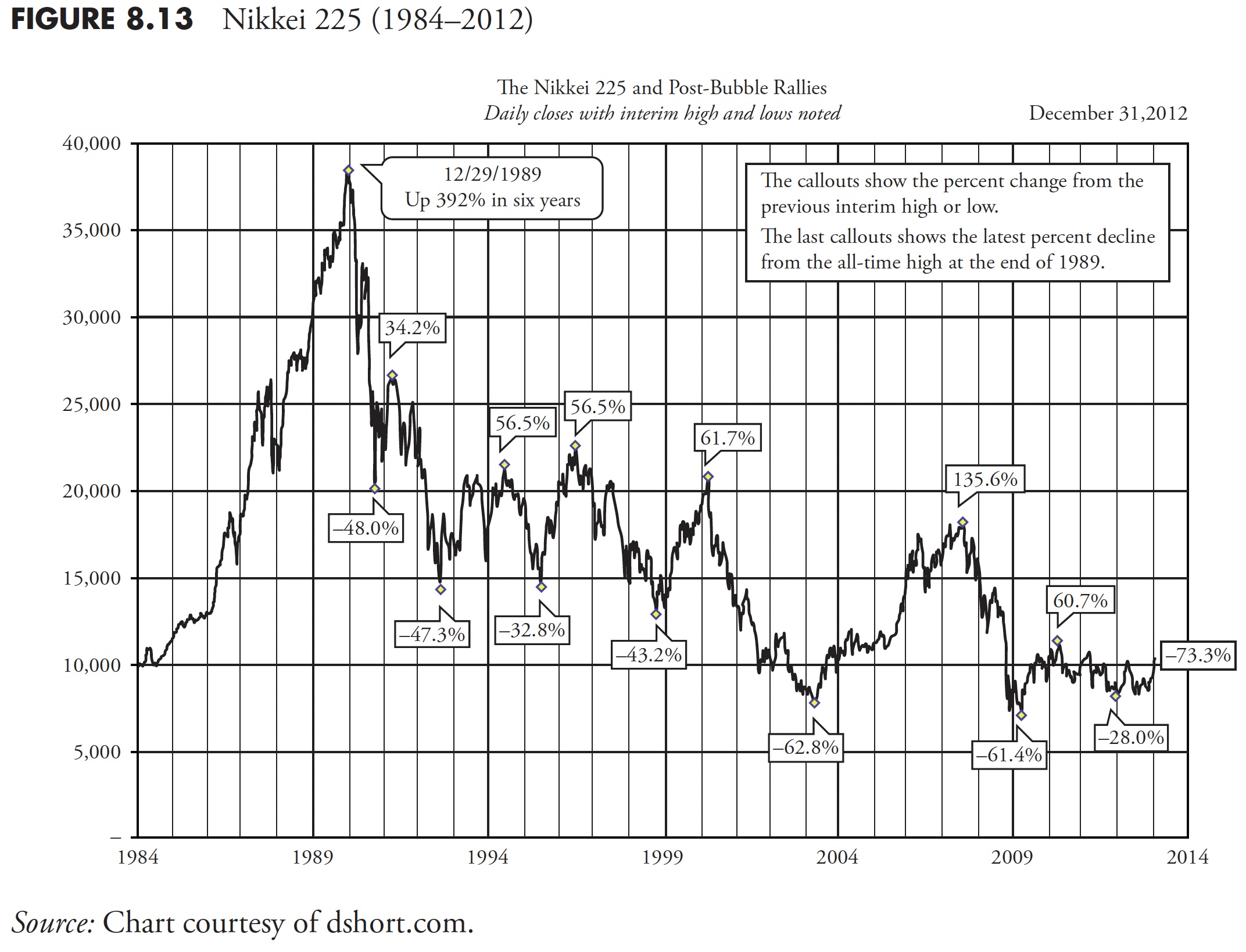
Lastly, please discover that Determine 8.13 covers roughly 30 years of knowledge and that the purpose on the appropriate finish (most up-to-date worth) is roughly equal to the start line again within the mid-Nineteen Eighties; definitely the misplaced three many years. Purchase and Maintain is Purchase and Hope.
Market Returns
It’s all the time good to see how the markets have carried out prior to now. With the arrival of the web, globalization, minute-by-minute information, traders have a pure tendency to deal with the brief time period. With no information of the long-term efficiency of the markets, that short-term orientation could cause one to be completely out of contact with the truth that the market doesn’t all the time go up. The next charts will present annualized returns for the S&P 500 worth, complete return, and inflation-adjusted complete return over varied durations. A lot of these charts are often known as rolling return charts. For instance, utilizing the 10-year annualized rolling return, the info begins in 1928, so the primary knowledge level wouldn’t be till 1938 and be the 10-year annualized return from 1928 to 1938. The following knowledge level could be for the 10-year interval from 1929 to 1939, the third from 1930 to 1940, and so forth.
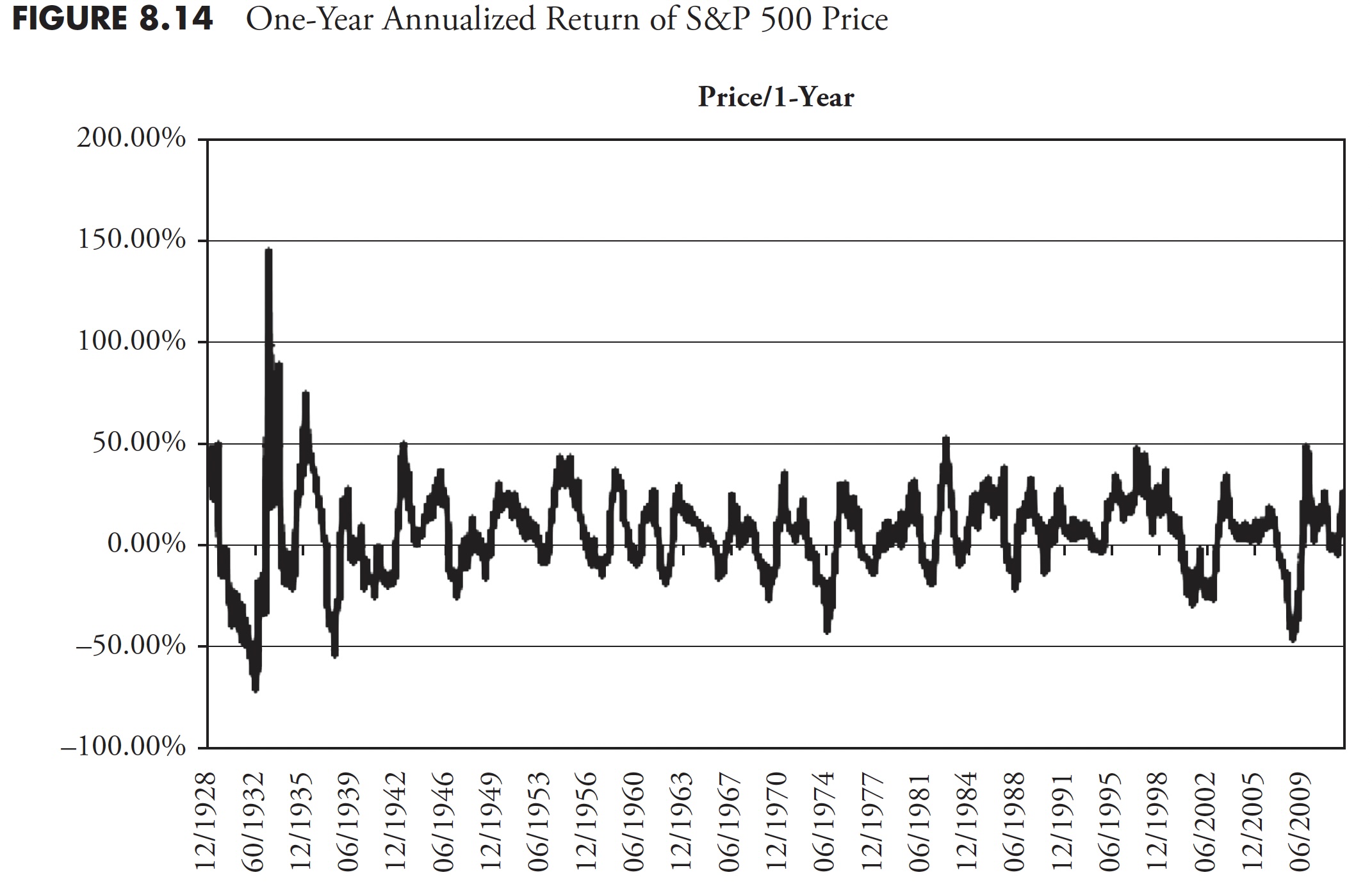
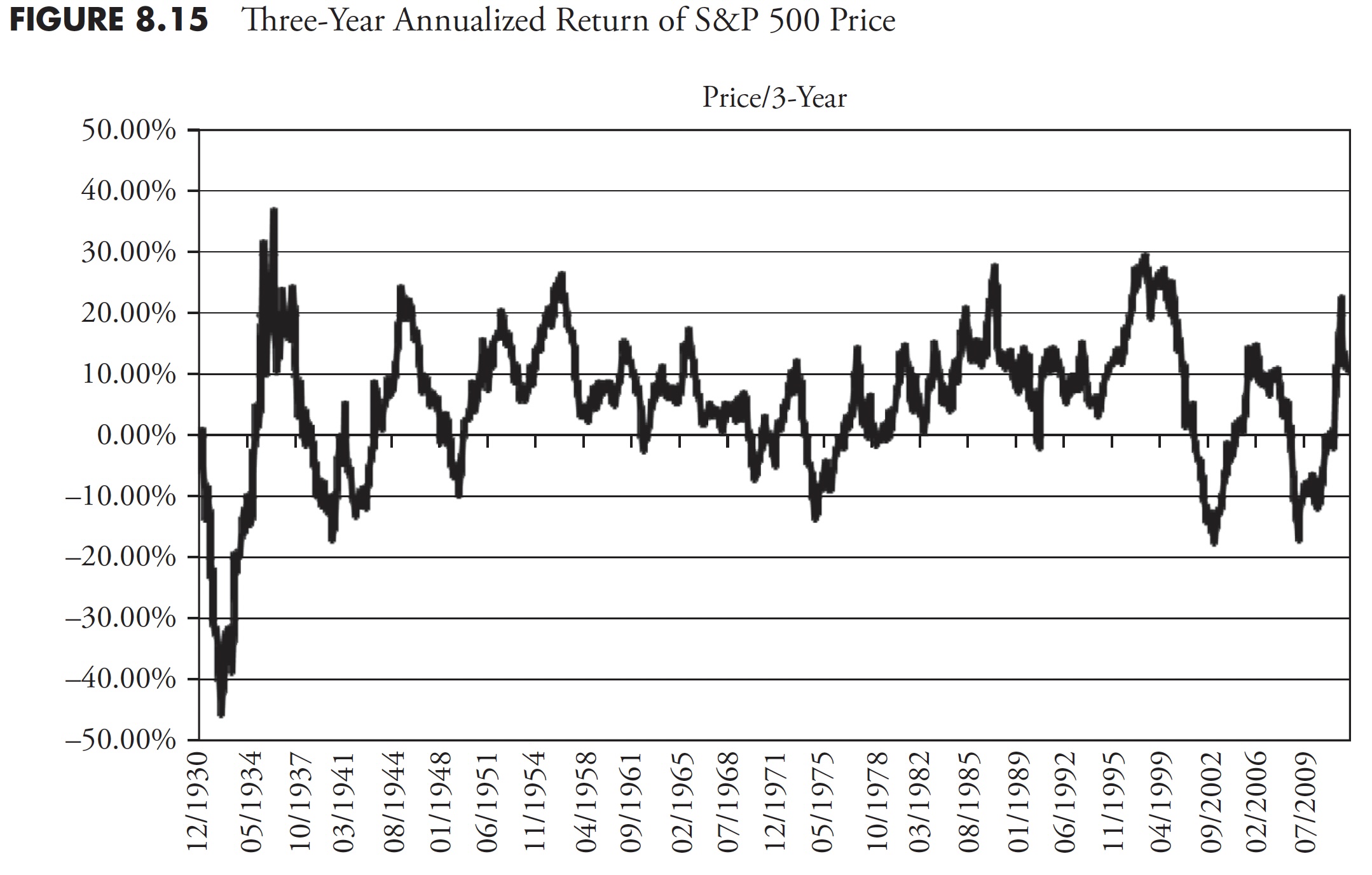
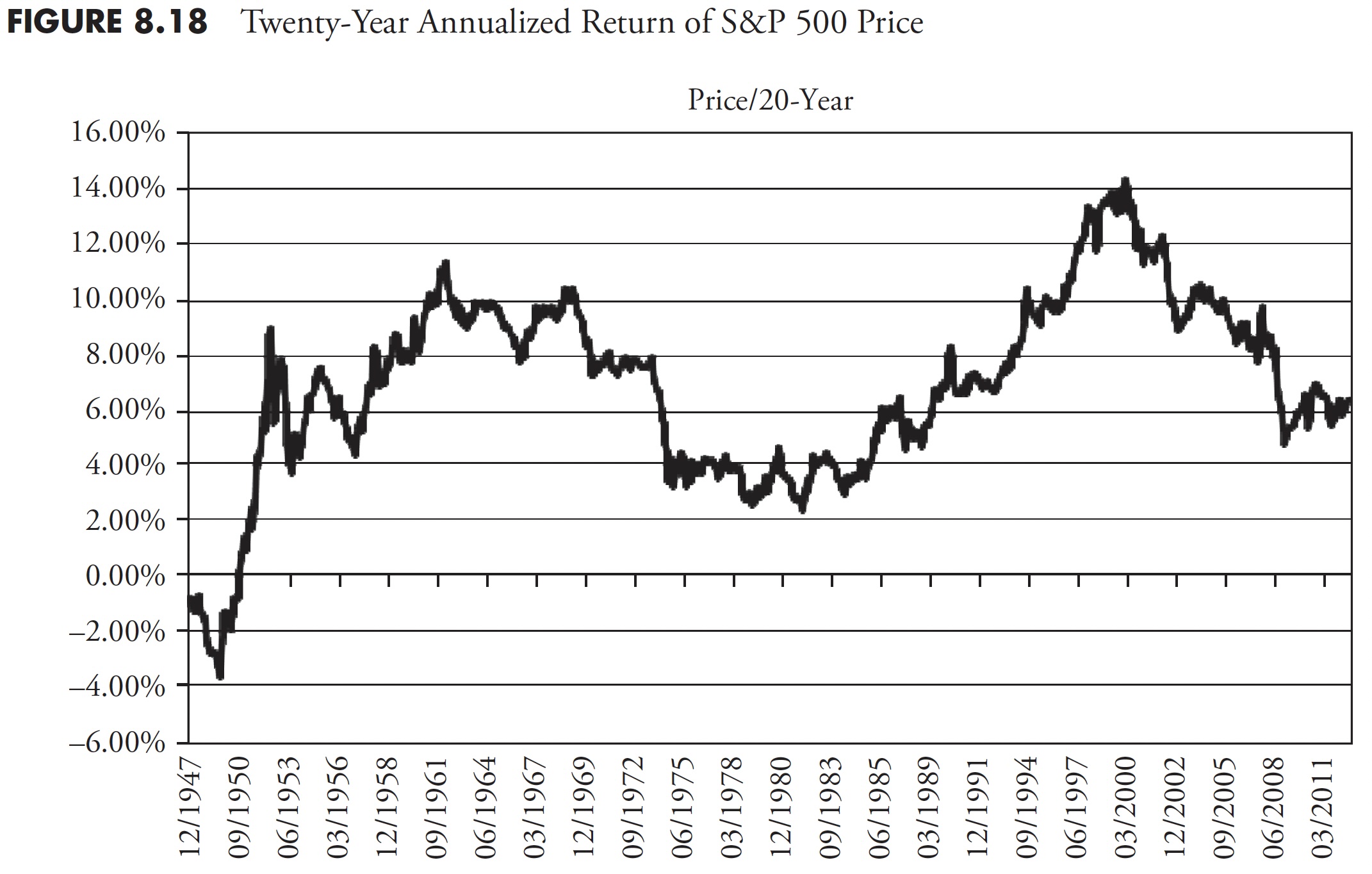
Determine 8.14 reveals the 1-year annualized return for the S&P worth. It must be apparent that one-year returns are all over, oscillating between highs within the 40 % to 50 % vary, and lows within the -15 % to -25 % vary. Following Determine 8.14 are the 3-year (Determine 8.15), 5-year (Determine 8.16), 10-year (Determine 8.17), and 20-year (Determine 8.18) charts of annualized returns, with the typical for all the info proven within the chart caption. Following the 20-year chart is an extra evaluation for the 20-year interval.
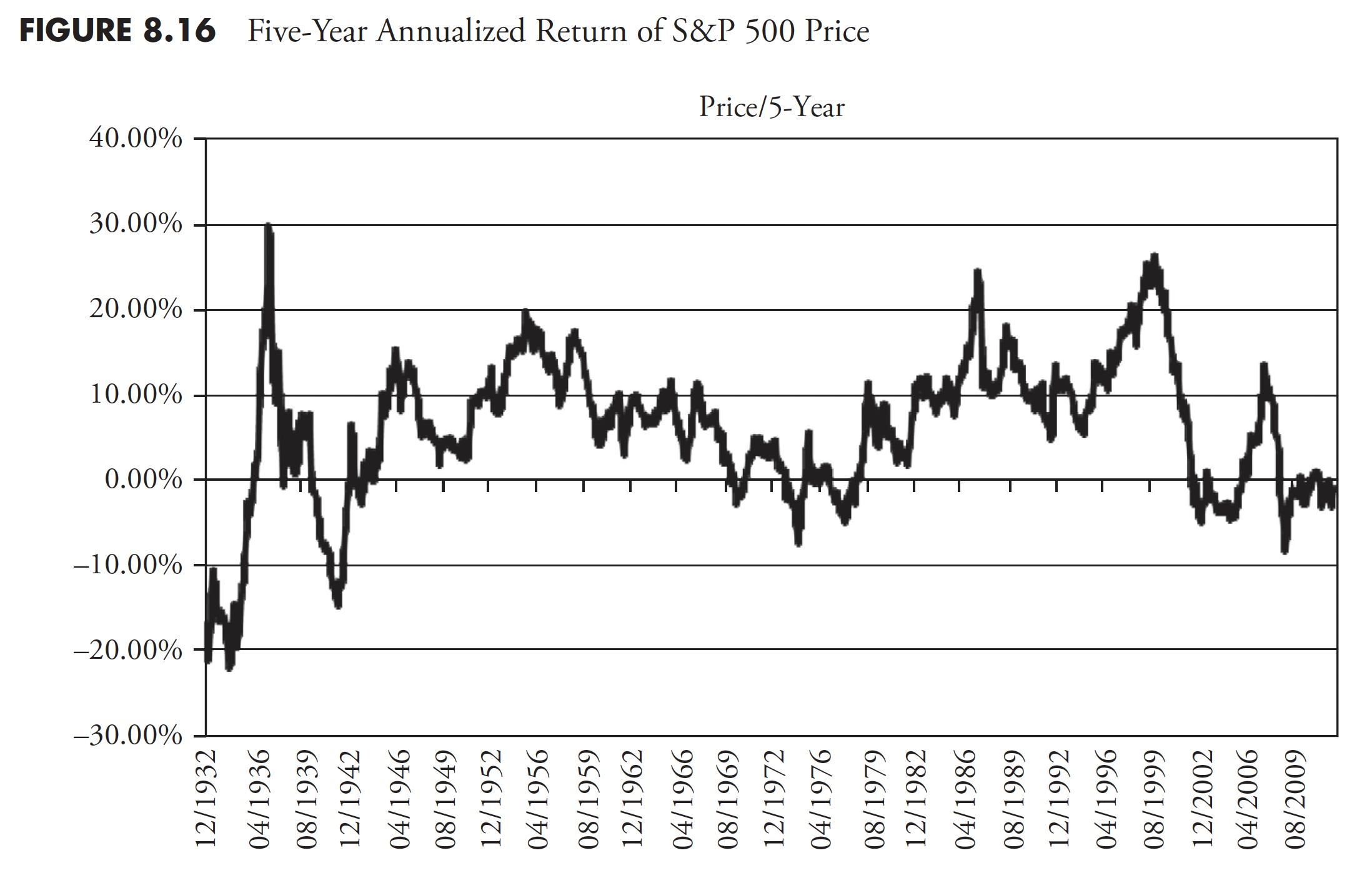
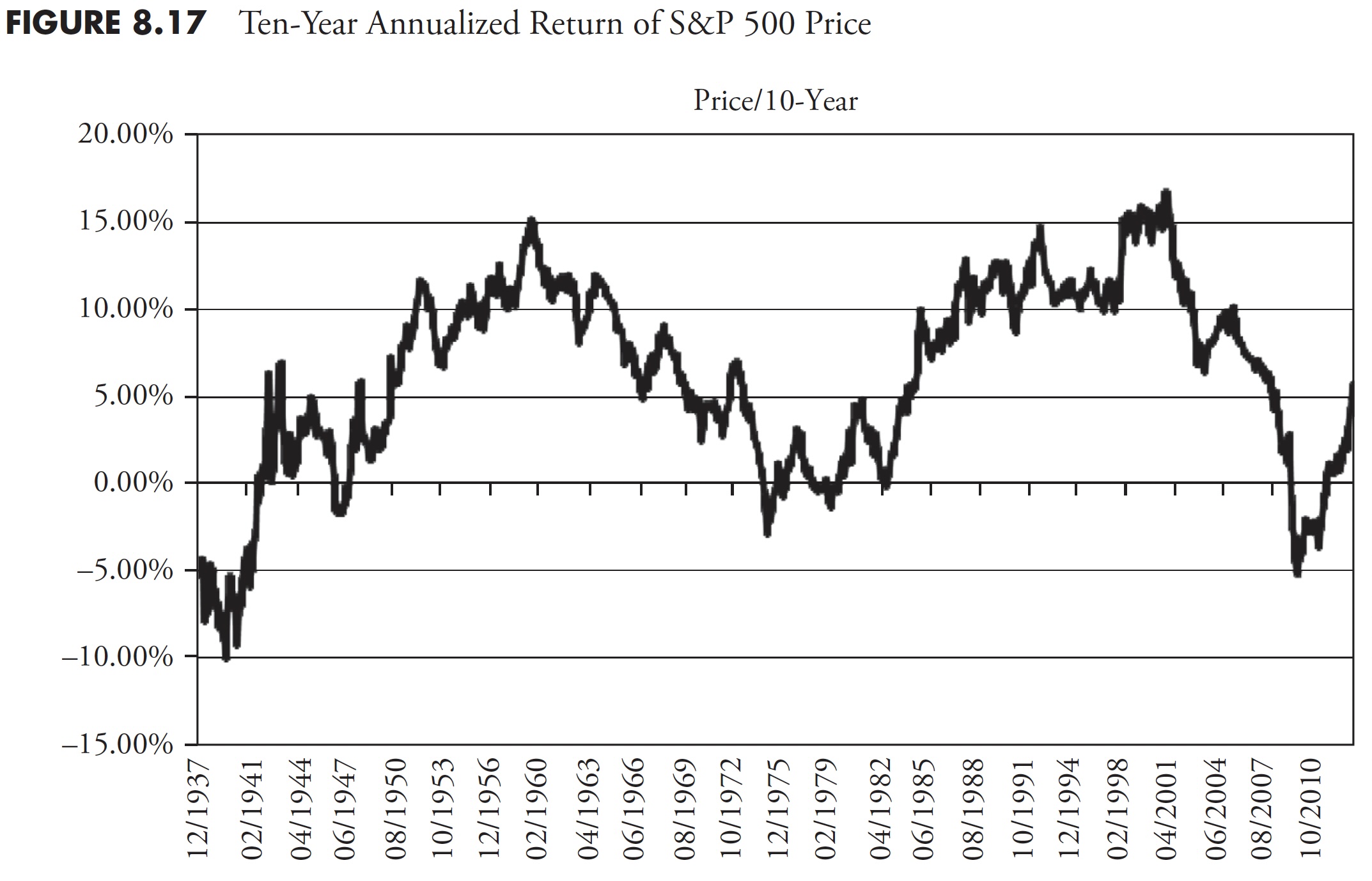
The ten-year return chart now clearly reveals up-and-down traits within the knowledge (see Determine 8.17).
The 20-year rolling return chart (Determine 8.18) continues to cut back the short-term volatility within the chart, and the up-and-down traits change into clear.
Since I adamantly consider that almost all traders have about 20 years to actually put cash away in a severe method for retirement, the next two charts present returns over 20 years for complete return (Determine 8.19) and inflation-adjusted complete return (Determine 8.20).
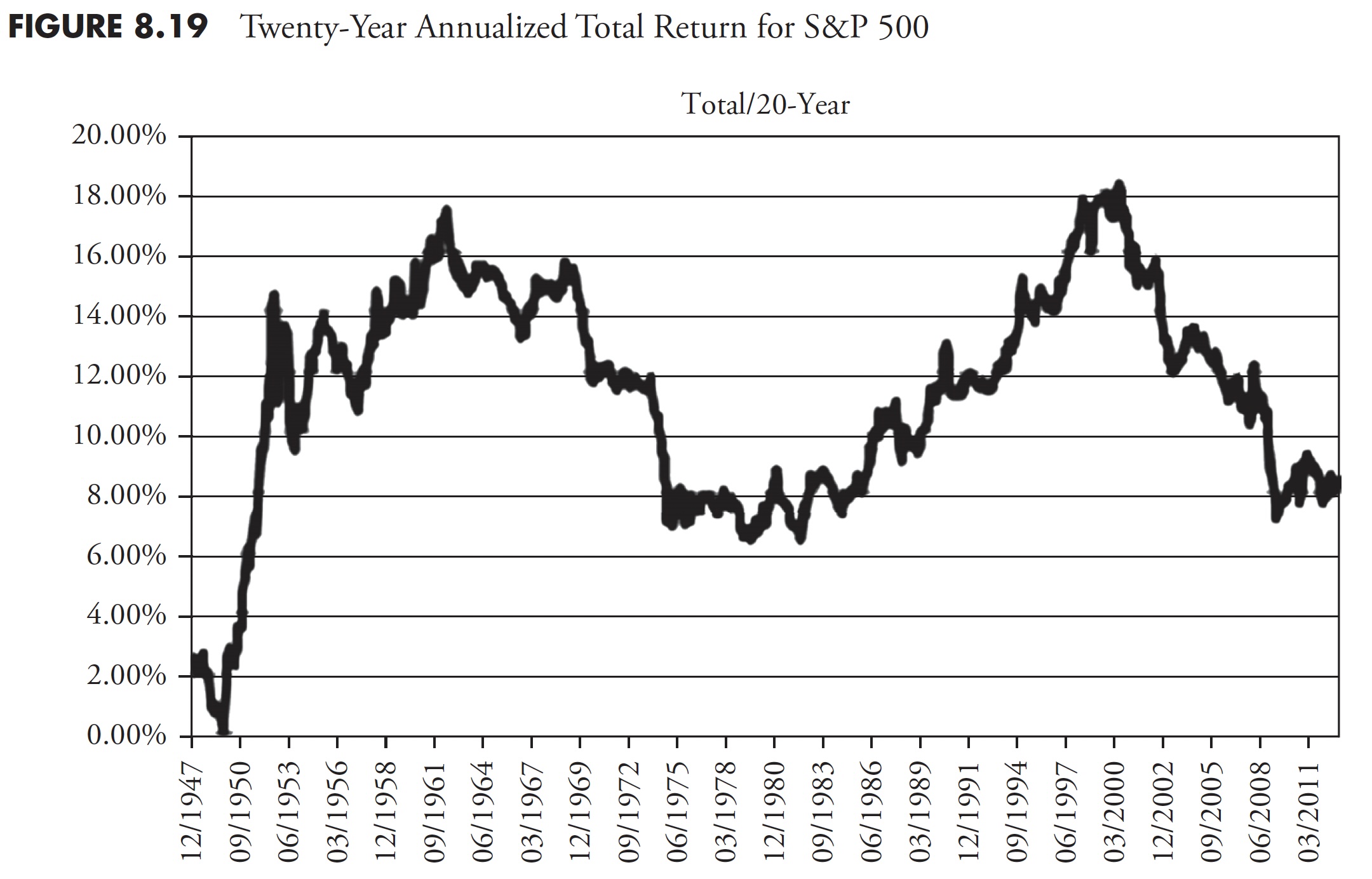
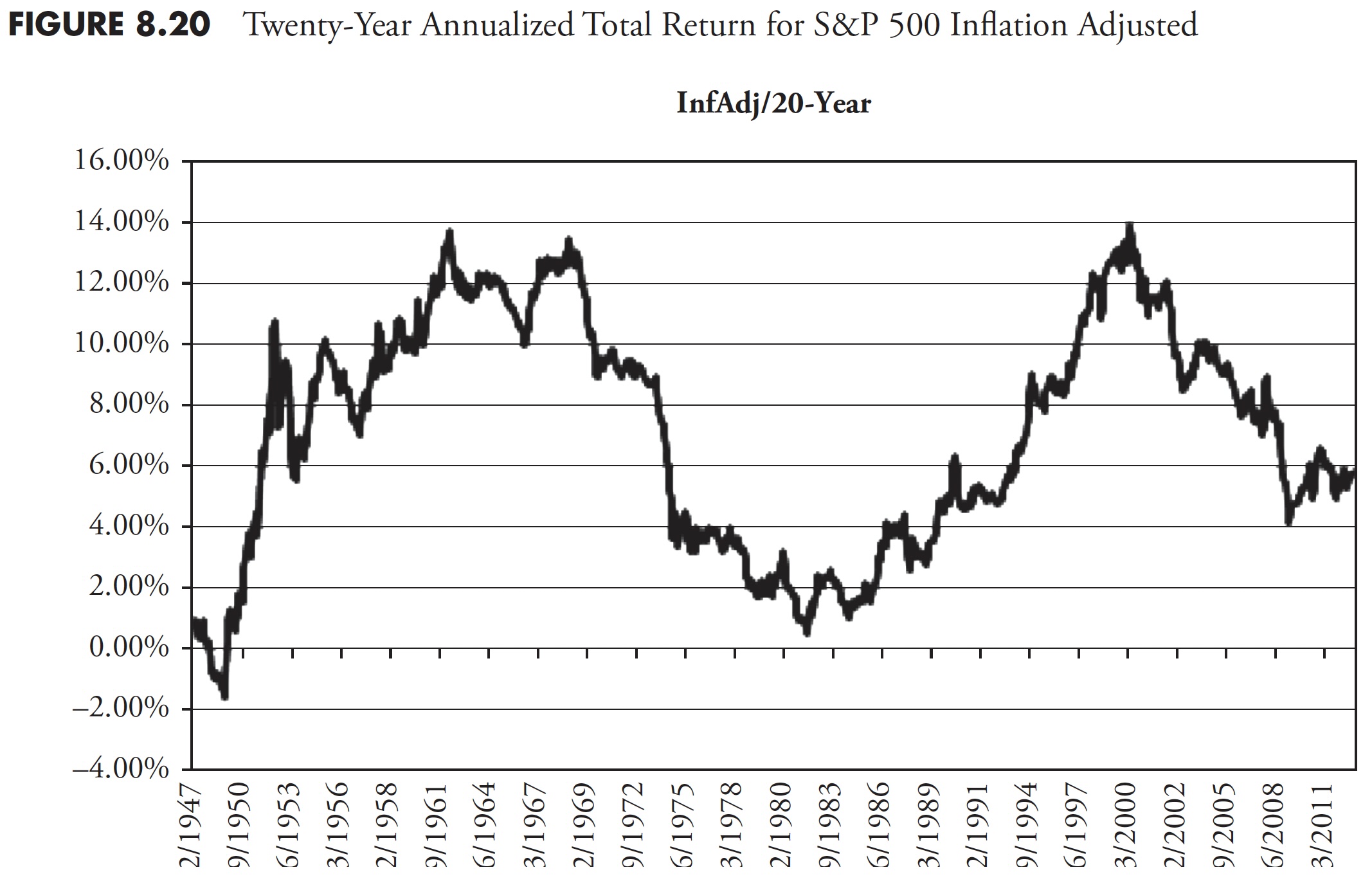
For many evaluation, the Worth chart is greater than ample. On the earth of finance, there may be an nearly common demand for the Complete Return chart; nonetheless, I believe that if you’ll insist on Complete Return, you need to then additionally insist on Inflation-Adjusted Complete Return. Utilizing the three previous 20-year charts and the averages proven, you’ll be able to see that the typical for Worth is 6.97 %, Complete Return is 11.32 %, and Inflation-Adjusted Complete Return is 7.19 %. What this says is that the impact of together with dividends (Complete Return) and the impact of Inflation typically neutralize one another.
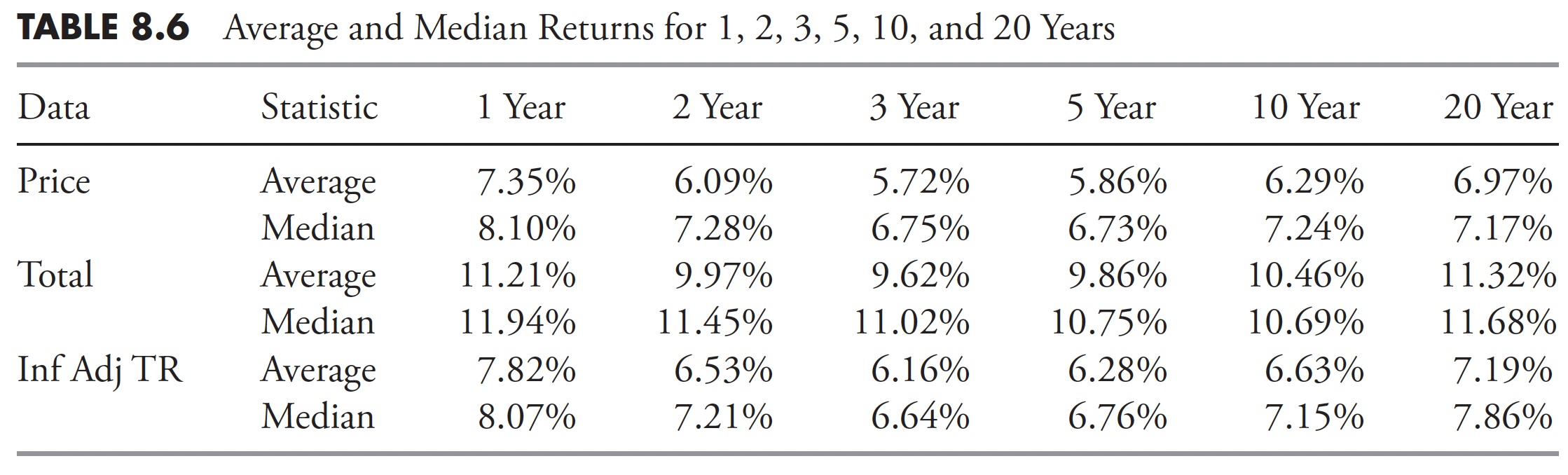
Desk 8.6 reveals the annualized returns for the S&P 500 for worth, complete return, and inflation-adjusted complete return for the next durations: 1-year, 2-year, 3-year, 5-year, 10-year, and 20-year.
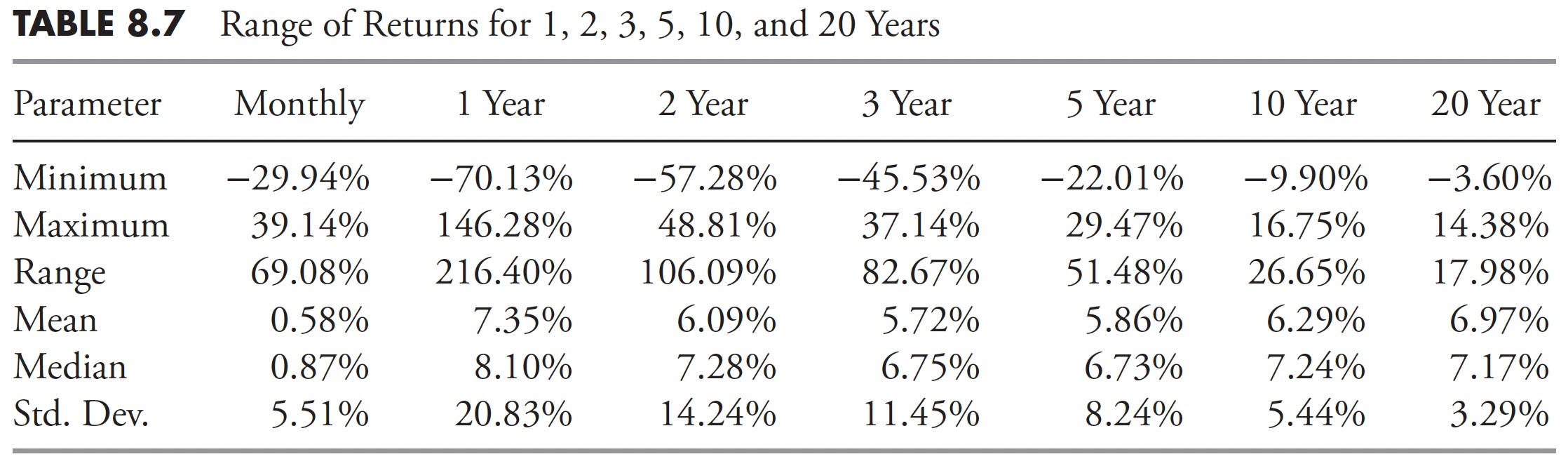
Desk 8.7 reveals the minimal and most returns, together with the vary of returns, their imply, median, and variability about their imply (Normal Deviation).
Distribution of Returns
The vary of return knowledge could be very simple to calculate as a result of it’s merely the distinction between the most important and the smallest values in a knowledge set. Thus, vary, together with any outliers, is the precise unfold of knowledge. Vary equals the distinction between highest and lowest noticed values. Nonetheless, an excessive amount of data is ignored when computing the vary, as a result of solely the most important and smallest knowledge values are thought-about. The vary worth of a knowledge set is vastly influenced by the presence of only one unusually massive or small worth (outlier). The drawback of utilizing vary is that it doesn’t measure the unfold of many of the values—it solely measures the unfold between highest and lowest values. Because of this, different measures are required in an effort to give a greater image of the info unfold. The month-to-month returns for the S&P 500 start with December 1927, so, as of December 2012, there are 1,020 months (85 years) of knowledge.
Further charts present the distribution of knowledge in varied methods utilizing the 20-year annualized returns of the S&P 500 inflation-adjusted complete return knowledge for rolling 20-year durations. Twenty-year returns from the S&P 500 with 1,020 months of knowledge would yield 778 knowledge factors. Return distributions might be considered like this: Every bar represents the proportion of the returns that meet a proportion division of the info, mathematical division of the info, or statistical division of the info. The next are definitions of the varied distribution strategies, as proven within the title of the next figures.
- Decile. One in every of 10 teams containing an equal variety of the gadgets that make up a frequency distribution. The vary of returns is set by the distinction between the minimal and most returns within the sequence, then divided by 10 to create 10 equal teams.
- Quartile. The calculation is much like decile (above), however with solely 4 groupings.
(Notice: This use of decile and quartile doesn’t comply with the usual definition or calculation technique typically utilized in statistics.)
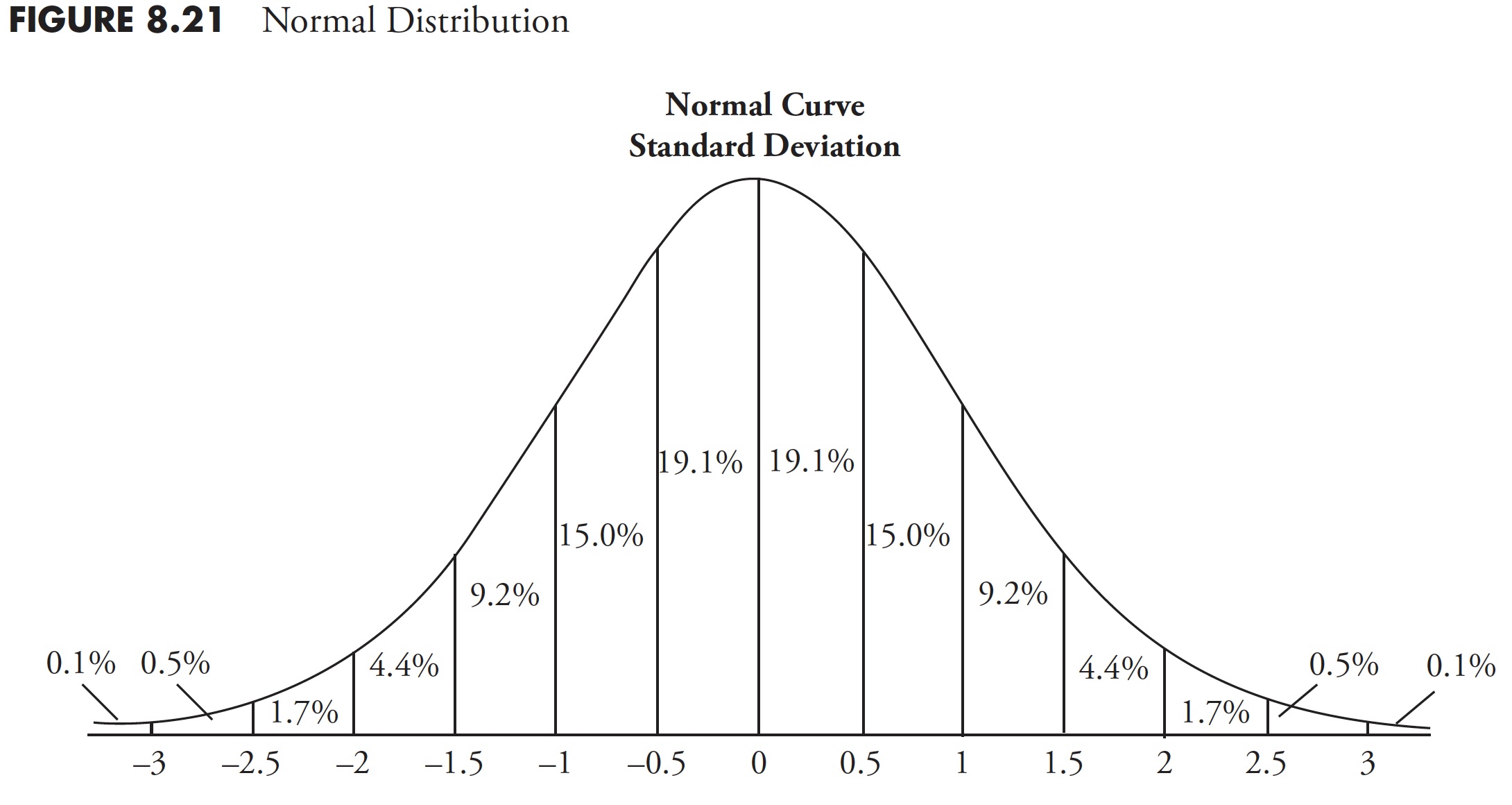
- Normal deviation. A statistical measure of the quantity by which a set of values differs from the arithmetical imply, equal to the sq. root of the imply of the variations’ squares. Determine 8.21 reveals the proportion of the info that’s included in a normal deviation. You may see that the imply is the height and that 68.2 % of the info is inside one normal deviation from the imply, and 95.4 % of the info is inside two normal deviations of the imply.
- Proportion. A proportion acknowledged by way of one-hundredths that’s calculated by multiplying a fraction by 100.
Determine 8.22 reveals the 20-year rolling returns utilizing inflation-adjusted complete return knowledge distributed by quartiles. From the chart, you’ll be able to see that 13.24 % of the returns fall into the primary quartile, or lowest 25 %, of the info, 28.15 % within the second, 32.90 % within the third, and 25.71 % within the fourth quartile or highest 25 % of the info.
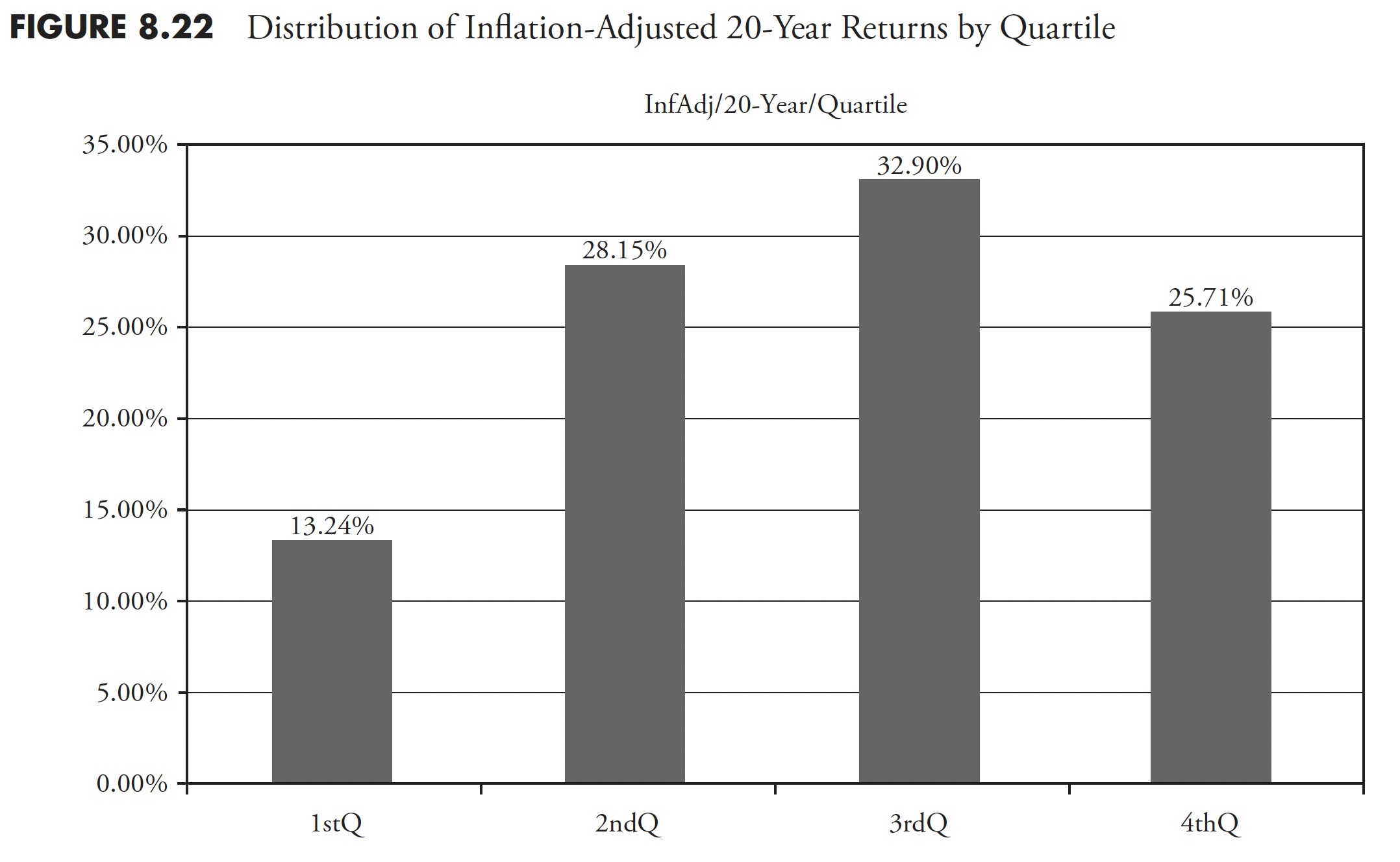
Determine 8.23 reveals the identical knowledge, however in a decile distribution the place every bar represents 10 % of the variety of knowledge gadgets. For instance, 8.23 % of the info fell within the highest 10 % of the info.
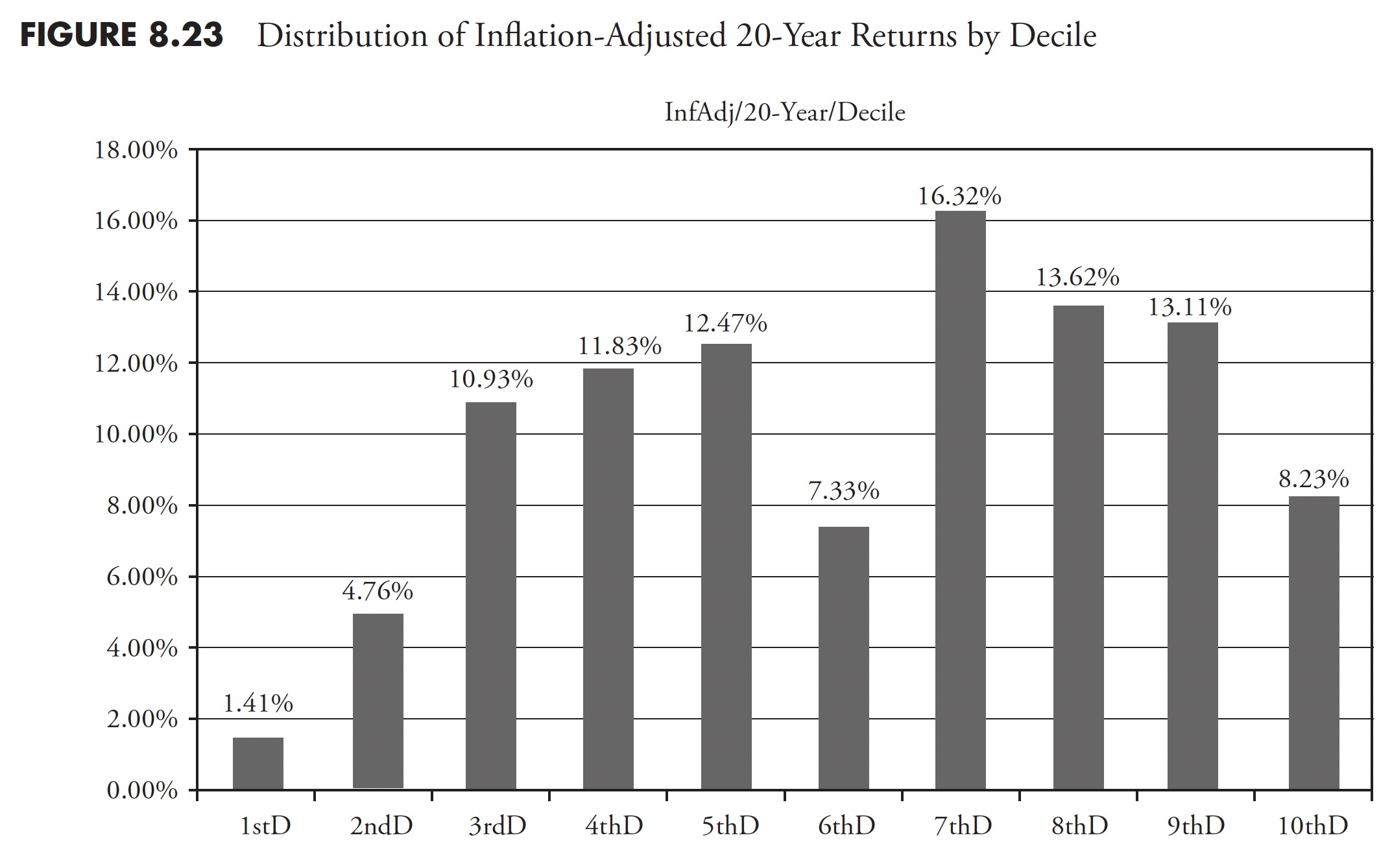
Determine 8.24 reveals the distribution of the info based mostly on variance from the imply or normal deviation. You may see that the 2 center bars every characterize 34.1 % of the info (68.2 % complete) that’s one normal deviation from the imply. For instance, 33.68 % of the 20-year rolling returns knowledge was inside one normal deviation above the imply of all the info. You too can surmise that the 2 bars on the appropriate characterize 50 % of all the info and 53.86 % (33.68 + 20.18) of the returns. Oversimplifying this, one then is aware of that there have been extra returns larger than the imply. Nonetheless, there may be an asymmetrical distribution between the returns which might be outdoors of 1 normal deviation from the imply, with the bigger proportion to the draw back.
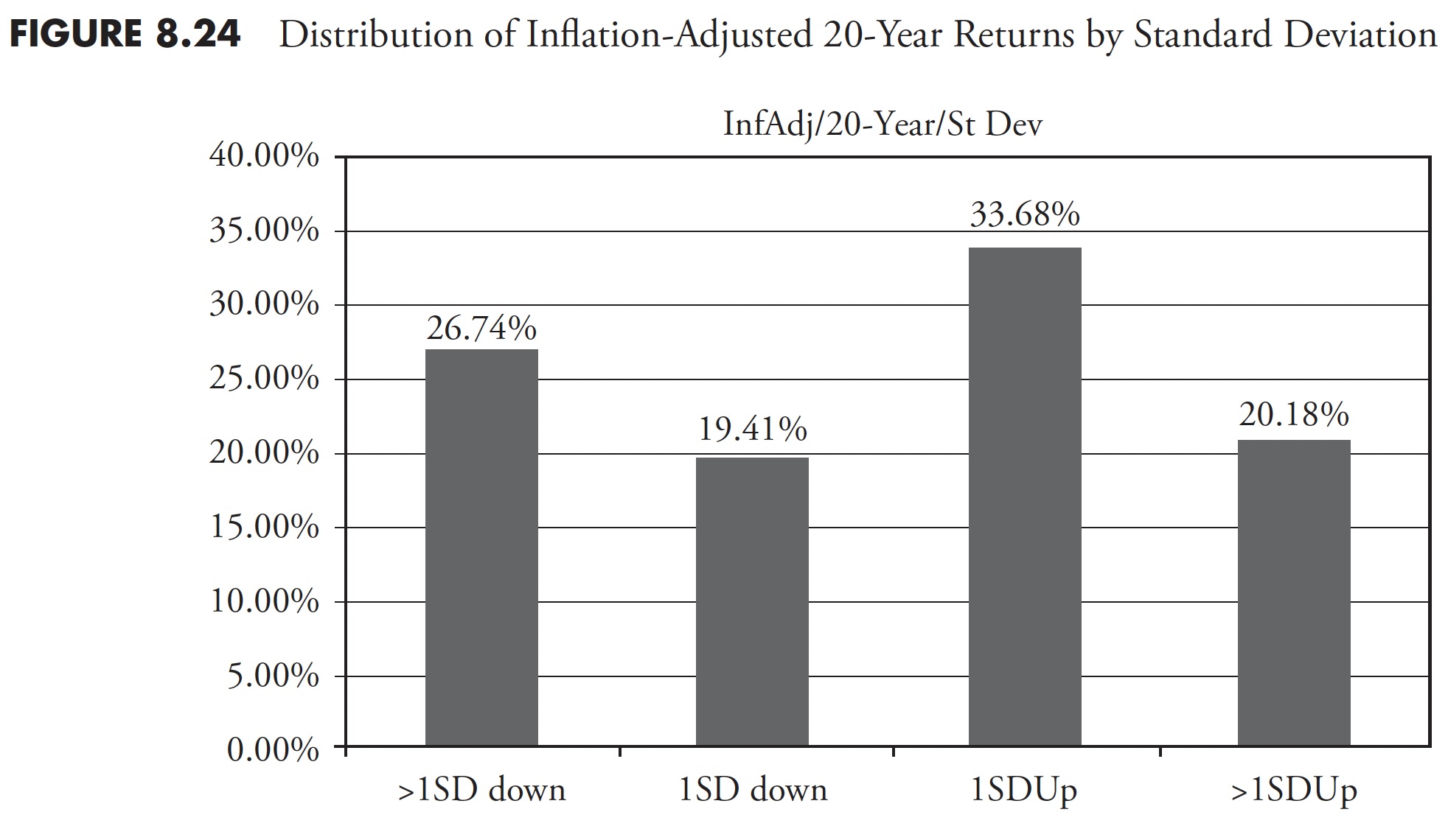
Determine 8.25 reveals the 20-year rolling returns of the S&P 500 inflation-adjusted complete return inside proportion ranges. The bar on the left reveals all of the returns of lower than 8 %, which accounted for greater than 50 % of all returns (51.41 %), whereas the bar on the appropriate reveals returns of larger than 12 %, accounted for less than 11.31 % of all returns. The bar within the center is the vary of returns between 8 % and 12 %, which accounted for 37.28 % of all returns. Recall the dialogue in Chapter 4 on the deception of common, and as soon as once more the typical 8 % to 12 % return isn’t common.
When the market begins to say no considerably, it’s not the identical as when somebody yells “hearth” in a theater. In a theater, everyone seems to be working for the exits. In an enormous decline out there, you’ll be able to run for the exits, however first it’s important to discover somebody to switch you—you should discover a purchaser. Massive distinction! This chapter has tried to stay to what I consider are market info and important data you need to perceive in regard to how markets work and have labored prior to now. If one doesn’t know market historical past, it could be very troublesome to maintain a deal with what the probabilities are sooner or later.
This concludes the primary part of this e-book, the place I’ve tried to point out you the numerous fashionable beliefs in regards to the market which might be utilized by academia and Wall Road to assist promote their merchandise. Half I additionally wraps up with what I consider to be truisms in regards to the market. Half II has an introductory chapter on technical evaluation and is adopted by two chapters on in depth analysis into development dedication and danger/drawdowns.
Thanks for studying this far. I intend to publish one article on this sequence each week. Cannot wait? The e-book is on the market right here.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

