[ad_1]
This text was initially featured on The Dialog.
With the arrival of spring in North America, many individuals are gravitating to the gardening and landscaping part of residence enchancment shops, the place shows are overstocked with eye-catching seed packs and benches are full of potted annuals and perennials.
However some vegetation that when thrived in your yard might not flourish there now. To know why, look to the U.S. Division of Agriculture’s latest replace of its plant hardiness zone map, which has lengthy helped gardeners and growers determine which vegetation are most definitely to thrive in a given location.
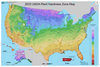
Evaluating the 2023 map to the earlier model from 2012 clearly reveals that as local weather change warms the Earth, plant hardiness zones are shifting northward. On common, the coldest days of winter in our present local weather, based mostly on temperature data from 1991 by means of 2020, are 5 levels Fahrenheit (2.8 Celsius) hotter than they have been between 1976 and 2005.
In some areas, together with the central Appalachians, northern New England and north central Idaho, winter temperatures have warmed by 1.5 hardiness zones – 15 levels F (8.3 C) – over the identical 30-year window. This warming adjustments the zones through which vegetation, whether or not annual or perennial, will in the end reach a local weather on the transfer.

As a plant pathologist, I’ve devoted my profession to understanding and addressing plant well being points. Many stresses not solely shorten the lives of vegetation, but additionally have an effect on their development and productiveness.
I’m additionally a gardener who has seen firsthand how warming temperatures, pests and illness have an effect on my annual harvest. By understanding local weather change impacts on plant communities, you may assist your backyard attain its full potential in a warming world.
Hotter summers, hotter winters
There’s no query that the temperature pattern is upward. From 2014 by means of 2023, the world skilled the 10 hottest summers ever recorded in 174 years of local weather knowledge. Just some months of sweltering, unrelenting warmth can considerably have an effect on plant well being, particularly cool-season backyard crops like broccoli, carrots, radishes and kale.

Winters are additionally warming, and this issues for vegetation. The USDA defines plant hardiness zones based mostly on the coldest common annual temperature in winter at a given location. Every zone represents a 10-degree F vary, with zones numbered from 1 (coldest) to 13 (warmest). Zones are divided into 5-degree F half zones, that are lettered “a” (northern) or “b” (southern).
For instance, the coldest hardiness zone within the decrease 48 states on the brand new map, 3a, covers small pockets within the northernmost elements of Minnesota and has winter excessive temperatures of -40 F to -35 F. The warmest zone, 11b, is in Key West, Florida, the place the coldest annual lows vary from 45 F to 50 F.
On the 2012 map, northern Minnesota had a way more intensive and steady zone 3a. North Dakota additionally had areas designated on this identical zone, however these areas now have shifted utterly into Canada. Zone 10b as soon as lined the southern tip of mainland Florida, together with Miami and Fort Lauderdale, however has now been pushed northward by a quickly encroaching zone 11a.
Many individuals purchase seeds or seedlings with out enthusiastic about hardiness zones, planting dates or illness dangers. However when vegetation need to cope with temperature shifts, warmth stress and illness, they are going to finally battle to outlive in areas the place they as soon as thrived.
Profitable gardening continues to be potential, although. Listed here are some issues to think about earlier than you plant:
Annuals versus perennials
Hardiness zones matter far much less for annual vegetation, which germinate, flower and die in a single rising season, than for perennial vegetation that final for a number of years. Annuals sometimes keep away from the deadly winter temperatures that outline plant hardiness zones.
In reality, most annual seed packs don’t even record the vegetation’ hardiness zones. As a substitute, they supply sowing date pointers by geographic area. It’s nonetheless necessary to observe these dates, which assist be certain that frost-tender crops are usually not planted too early and that cool-season crops are usually not harvested too late within the yr.
Person-friendly perennials have broad hardiness zones
Many perennials can develop throughout vast temperature ranges. For instance, hardy fig and hardy kiwifruit develop effectively in zones 4-8, an space that features many of the Northeast, Midwest and Plains states. Raspberries are hardy in zones 3-9, and blackberries are hardy in zones 5-9. This eliminates lots of guesswork for many gardeners, since a majority of U.S. states are dominated by two or extra of those zones.
However, it’s necessary to concentrate to plant tags to keep away from choosing a spread or cultivar with a restricted hardiness zone over one other with higher flexibility. Additionally, take note of directions about correct solar publicity and planting dates after the final frost in your space.
Fruit timber are delicate to temperature fluctuations
Fruit timber have two elements, the rootstock and the scion wooden, which can be grafted collectively to kind a single tree. Rootstocks, which consist primarily of a root system, decide the tree’s measurement, timing of flowering and tolerance of soil-dwelling pests and pathogens. Scion wooden, which helps the flowers and fruit, determines the fruit selection.
Most commercially out there fruit timber can tolerate a variety of hardiness zones. Nevertheless, stone fruits like peaches, plums and cherries are extra delicate to temperature fluctuations inside these zones – significantly abrupt swings in winter temperatures that create unpredictable freeze-thaw occasions.
These seesaw climate episodes have an effect on all sorts of fruit timber, however stone fruits look like extra vulnerable, presumably as a result of they flower earlier in spring, have fewer hardy rootstock choices, or have bark traits that make them extra weak to winter harm.
Perennial vegetation’ hardiness will increase by means of the seasons in a course of referred to as hardening off, which circumstances them for harsher temperatures, moisture loss in solar and wind, and full solar publicity. However a too-sudden autumn temperature drop could cause vegetation to die again in winter, an occasion often called winter kill. Equally, a sudden spring temperature spike can result in untimely flowering and subsequent frost kill.
Pests are shifting north too
Crops aren’t the one organisms constrained by temperature. With milder winters, southern insect pests and plant pathogens are increasing their ranges northward.
One instance is Southern blight, a stem and root rot illness that impacts 500 plant species and is brought on by a fungus, Agroathelia rolfsii. It’s typically regarded as affecting sizzling Southern gardens, however has turn out to be extra commonplace not too long ago within the Northeast U.S. on tomatoes, pumpkins and squash, and different crops, together with apples in Pennsylvania.
Different plant pathogens might benefit from milder winter temperatures, which ends up in extended saturation of soils as an alternative of freezing. Each vegetation and microbes are much less energetic when soil is frozen, however in moist soil, microbes have a chance to colonize dormant perennial plant roots, resulting in extra illness.
It may be difficult to just accept that local weather change is stressing a few of your backyard favorites, however there are literally thousands of forms of vegetation to go well with each your pursuits and your hardiness zone. Rising vegetation is a chance to admire their flexibility and the options that allow a lot of them to thrive in a world of change.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

